A height weight chart is a ratio used to assess whether a person’s weight falls within a healthy range relative to their height. Height and weight are important health factors that can indicate overall health and risk for certain diseases. Maintaining a proper height weight ratio is important for good health; the correct ratio can be determined by consulting a doctor who can give or refer to a height weight chart, showing you weight ranges corresponding to different heights. To read a height weight chart, locate your height and find the corresponding weight range considered healthy for that height.
Studying the height weight chart helps people and their doctors see how weight changes over time, making it easier to make healthy choices about food and exercise. This chart also shows what a healthy weight looks like and encourages good habits for staying healthy.
What is a Height Weight Chart?
A height weight chart assesses whether an individual’s weight falls within a healthy range relative to height. To determine if you’re at a healthy weight for your height, healthcare providers use height and weight charts. These charts also help track children’s growth, manage weight, and guide weight loss efforts. Your height and weight are measured and compared to these charts during checkups. However, it’s important to remember that these charts are only part of assessing health. Everyone’s health needs differ, so no single number or measurement applies to everyone. There aren’t really different types of weight according to height chart, but there are ways to consider them and their limitations:
- BMI Charts
- Head circumference
- Waist circumference
- Age-Adjusted Charts
- Body Composition Measurements
What is Ideal Height and Weight for Men, Women and Children?
The ideal height and weight for men, women, and children can vary based on several factors, including age, gender, body composition, and overall health. Height and weight are commonly used as indicators of overall health and may be assessed using growth charts, body mass index (BMI), or other measurements.
Ideal Height and Weight for Men
An NCBI article in 2015 titled “Height and Body Mass on the Mating Market” classifies men’s heights into six categories: very short, short, average, tall, very tall, and extremely tall. What we need to focus on is that when we compare height and weight, weight is the variable that you can control to a greater extent than your height. So, if a man’s height is 4’5 to 5 feet, then the ideal weight should be 28 Kg to 53 kg. In the other extreme, if the height is between 5’5 and 6’0 feet, then the weight shall be 55 kgs to 90 kgs. For a more specified range of the ideal height and weight for men, refer to the specific sections of this blog.
Ideal Height and Weight for Women
The ideal height and weight for women can vary significantly based on individual factors such as genetics, body composition, and overall health. While some women may naturally have a smaller frame and lower body weight, others may have a larger build or higher muscle mass. Additionally, factors like age, hormonal fluctuations, and lifestyle choices can all impact a woman’s weight and body composition over time. According to the research, if a woman is between 4’5 and 5’0 feet, then the weight shall be not more than 50 kgs and not less than 28.5 kgs. The other extreme is that if the height is 5’9 to 6’0 feet, the weight range lies between 60 kgs to 80 kgs.
Ideal Height and Weight for Children
The very first step is to measure the height and weight of your child. The ideal body weight for children can be then calculated using the following formulas suggested by the NIH:
- Children shorter than 5 feet: IBW in kilograms is calculated as ([height in inches]2 × 1.65)/1000
- Boys taller than 5 ft: Ideal body weight in kgs is calculated as 39 + (2.27 × [height in inches −)
- Girls taller than 5 feet: Ideal body weight in kgs is calculated as 42 + (2.27 × [height in inches −)
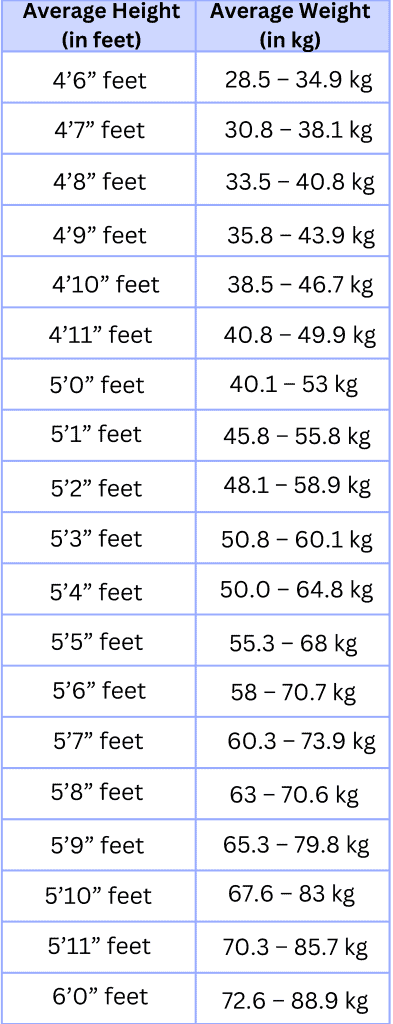
Height Weight Chart For Men
A ‘height and weight chart for men’ provides a general guideline for assessing whether a man’s weight is within a healthy range relative to his height. It consists of a chart listing various height ranges and corresponding weight ranges considered normal, overweight, or underweight based on body mass index (BMI) calculations. It’s important to note that while BMI and height and weight chart for men are helpful, but it doesn’t account for factors like muscle mass, so it may not be accurate for athletes or individuals with a high muscle-to-fat ratio.
Here’s a height and weight chart for men:
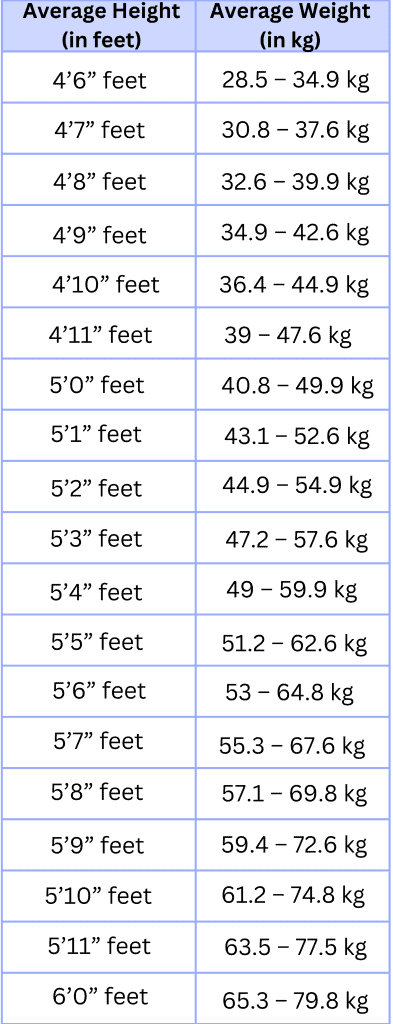
Height Weight Chart for Women
Women can use the ‘height and weight chart for women’ to evaluate their weight and overall health status. However, it’s essential to remember that individual health needs vary, and factors like age, activity level, and medical history should be considered when setting weight and fitness goals. Consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can offer personalised guidance on studying women’s height and weight charts and support for achieving a healthy weight.
Here’s a height and weight chart for women:
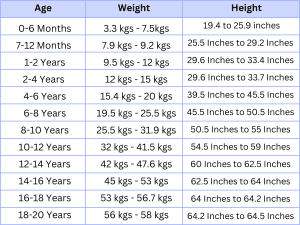
Height and Weight Chart for Children According to Age
A Height and Weight Chart according to age is a resource that can be used to understand individual growth and development. These charts are particularly useful for children and teens because they provide a comprehensive overview of the weight that corresponds to age, allowing for a more accurate evaluation of growth patterns.
Interpretation of Height Weight Chart
Interpreting the height weight chart is essential to understand whether an individual is underweight, overweight, or within a healthy weight range based on their height. Let’s define these categories with noteworthy points:
1. Healthy Weight Range
Height weight charts offer a range of healthy weights for different heights. Based on averages, this range helps determine if someone’s weight is healthy for their height. Those within this range typically have a healthy weight. Additionally, a healthy BMI falls between 18.5 to 24.9.
2. Underweight and Overweight Categories
Height weight charts also have categories for underweight and overweight based on BMI. Here’s the range:
- Underweight: BMI below 18.5.
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9.
If someone’s BMI is below a certain point, they might be labelled as underweight, and if it’s above a certain point, they could be labelled as overweight. These categories help spot people who might have health concerns because of their weight. But remember, BMI isn’t the whole health story.
3. Risk Assessment
Healthcare providers use height weight charts to assess an individual’s risk of certain health conditions associated with weight, such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Individuals falling outside the healthy weight range or BMI range may be at increased risk and require further evaluation and intervention. For example, individuals classified as overweight or obese may be advised to make lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, and managing stress to reduce their risk of weight-related health issues.
How to use a Height Weight Chart?
Using the weight according to height chart is an easy process that can help individuals assess whether or not their weight is within a healthy range based on their height. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use the chart effectively:
Step 1: Measure Your Height
Begin by measuring your height accurately. Use measuring tape or stand against a wall with a ruler to determine your height in feet, inches, or centimetres.
Step 2: Determine Your Weight
Measure your weight using a scale. For accurate results, weigh yourself without shoes and avoid wearing heavy clothing.
Step 3: Locate and Interpret Your Position on the Chart
Once you have your height and weight measurements, find the corresponding position on the height weight chart. The chart typically consists of a grid with height listed on one axis and weight on the other. Now, you can interpret the result with the same weight according to the height chart. In the previous section, we discussed three main categories: underweight, normal weight, and overweight.
Step 5: Consider Other Factors
While the height weight chart provides a general guideline, remember that individual variations exist. Muscle mass, body frame size, and age may influence your ideal weight range. Therefore, it’s essential to consider other measurement methods, such as the BMI calculator, body fat percentage, and waist-to-hip ratio, for a more comprehensive assessment.
Step 6: Goals
If you are underweight, overweight, or obese, it’s essential to set realistic weight management goals. Consult with healthcare professionals or certified fitness experts to develop a personalised plan, such as a 7 day diet plan for weight loss that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle adjustments to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
The weight according to height chart is a valuable tool to gain insights into whether your weight is proportionate to your height. It provides a starting point to assess your weight status.
Benefits of Using a Height and Weight Chart
The height weight chart is important in understanding and assessing an individual’s body composition and overall health. Let’s explore the key reasons why this height weight chart can help you;
1. Health Monitoring
- Regularly tracking weight using a weight according to height chart allows individuals to observe patterns and trends over time. By noting weight changes, individuals can identify potential health issues or fluctuations requiring further investigation.
- This ongoing monitoring provides valuable insight into overall health status and can help individuals and healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of diet changes or exercise programs.
2. Early Detection of Health Issues
- Height and weight charts are an early warning system for detecting health issues such as being overweight or overweight.
- Detecting these issues early allows individuals to take proactive steps to address them before they escalate into more severe health problems. For example, addressing weight gain through lifestyle changes can help prevent the development of obesity-related conditions like diabetes or heart disease.
3. Guidance for Healthy Weight Management
- Height and weight charts provide a reference point for individuals to determine their ideal weight range based on height.
- With this information, you can set realistic weight management goals like ‘How to lose 30 kgs weight?’ and make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- By regularly comparing your current weight to the recommended range, you can track your progress and adjust your approach to stay on course towards your goals.
4. Risk Assessment
- Height to weight ratio charts help you in assessing an individual’s risk of weight-related health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
- Healthcare providers can use height and weight data and other health indicators to develop personalised treatment plans and preventive strategies tailored to the individual’s specific needs and risk factors.
5. Provides Communication and Guidance
- Height and weight charts encourage communication between patients and healthcare providers by visually representing weight trends over time.
- Reviewing the height to weight ratio chart data with a healthcare professional allows you to discuss any changes or concerns and get personalised guidance for managing weight and overall health.
6. Motivation and Accountability
- Regularly tracking weight using a height and weight chart can provide motivation and accountability for individuals striving to achieve their health goals.
- Seeing progress over time, whether in maintaining a healthy weight or making positive changes to improve health outcomes, can boost confidence and encourage continued efforts to maintain a healthy weight and lifestyle.
- Additionally, sharing weight data and progress updates with supportive friends, family members, or online communities can encourage and reinforce motivation and accountability.
How is Weight According to Height Calculated?
Weight according to height chart can be calculated using various methods, the most common being the Body Mass Index (BMI). The BMI is a numerical value derived from an individual’s weight to their height. Here’s how the BMI is calculated and how it can be used to determine ideal weight:
BMI = Weight (kg) / (Height (m) * Height (m))
Steps to find out weight according to height chart using BMI calculations:
- Measure Your Weight: Use a scale to measure your weight in kilograms (kg).
- Measure Your Height: Use a measuring tape or a stadiometer to measure your height in meters (m).
- Calculate BMI: Plug your weight and height measurements into the BMI formula. Divide your weight in kilograms by the square of your height in meters.
Example: Suppose your weight is 70 kg and your height is 1.75 m.
BMI = 70 kg / (1.75 m * 1.75 m) = 22.86
Interpreting BMI:
Once you have calculated your BMI, you can interpret it using standard categories:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal Weight: BMI 18.5 – 24.9
- Overweight: BMI 25 – 29.9
- Obesity (Class I): BMI 30 – 34.9
- Obesity (Class II): BMI 35 – 39.9
- Obesity (Class III): BMI 40 or higher
While the BMI rate is a healthy and common choice, teenagers can use the height and weight chart according to age to assess their overall health and implement health programs accordingly.
Other ways to Determine Weight According to Height
When determining the ideal weight according to height chart, there are several alternative methods other than the height weight chart. While the Body Mass Index (BMI) is commonly used, there are other lesser-known and effective ways as well. Here are some other effective ways to measure average weight for height in kgs;
- BMI Calculator
- Waist-To-Hip Ratio (WHR)
- Waist-To-Height Proportion
- Percentage Of Body Fat
- Body Type And Waist Circumference
These methods are usually recommended for adults, so parents can use the height and weight chart according to age to monitor their child’s growth and ensure they are developing within the appropriate range. Let’s discuss each of them and see how you can find your average weight for height in kgs.
1. BMI Calculator
A BMI calculator is a simple tool that helps you check if your weight is healthy for your height. You enter your weight and height, and it calculates your BMI, which shows if you’re underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Here are the ranges you should note:
- If your BMI is less than 18.5, it falls within the underweight range.
- If your BMI is 18.5 to 24.9, it falls within the Healthy Weight range.
- If your BMI is 25.0 to 29.9, it falls within the overweight range.
- If your BMI is 30.0 or higher, it falls within the obese range.
BMI (Body Mass Index) is calculated by dividing an individual’s weight in kgs by the square of their height in meters. The formula is BMI = Weight (kg) divided by [Height (m) * Height (m)]. Example: Let’s say an individual weighs 70 kilograms, and their height is 1.75 meters.
- BMI = 70 kg / (1.75 m * 1.75 m) = 22.86
- A BMI of 22.86 falls within the “Normal Weight” range.
2. Waist-To-Hip Ratio (WtHR)
The waist-to-hip ratio (WtHR) is another valuable measurement resource besides the height-to-weight ratio chart. It determines the fat distribution in the body by dividing the waist circumference by the hip circumference. Those with excess fat around the waist (apple-shaped) may be at a greater risk of developing long-term diseases than those with stored fat around the hips and thighs (pear-shaped). Thus, measuring WHR is significant in knowing where we store fat because it can impact our health.
The formula is WHR = Waist Circumference (cm) divided by Hip Circumference (cm). For example, Consider a person with a waist circumference of 80 centimetres and a hip circumference of 100 centimetres.
- WHR = 80 cm / 100 cm = 0.8
- A WHR of 0.8 or less is generally considered healthy, indicating a lower risk of obesity-related health conditions.
3. Waist-To-Height Proportion
The waist-to-height ratio is a simple yet effective ratio to determine whether a person has a healthy body fat distribution. To calculate it, divide the waist circumference by the height. Experts suggest a waist-to-height ratio of 0.5 or less is associated with a lower risk of obesity-related health conditions.
To measure the waist-to-high ratio and find the average weight for height in kgs, divide the waist circumference by the individual’s height. Waist-to-Height Ratio = Waist Circumference (cm) / Height (cm). Example: For an individual with a waist circumference of 75 cm and a height of 165 cm:
- Waist-to-Height Ratio = 75 cm / 165 cm = 0.45
- A Waist-To-Height Ratio of 0.5 or less is associated with a lower risk of obesity-related health issues.
4. Percentage Of Body Fat
Measuring the percentage of body fat provides a more precise understanding of a person’s body composition. Various methods can be used, including bioelectrical impedance, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), or skinfold callipers. Knowing the percentage of body fat helps set realistic weight goals and assess overall health status.
Measuring the percentage of body fat requires specialised equipment like bioelectrical impedance, DEXA, or skinfold callipers, so you can’t do this at home to find the average weight for height in kgs.
5. Body Type And Waist Circumference
Thinking about body shape and waist size is important. Different body shapes need different healthy weights. Too much fat around the waist can cause health problems. Measuring waist size helps understand how much belly fat someone has and if it’s risky. There’s no exact way to do this, but knowing body shapes and checking waist size are important for finding the right weight. For example:
- For an individual with an “apple-shaped” body type, the waist circumference might be 90 cm.
- For another individual with a “pear-shaped” body type, their waist circumference might be 80 cm.
How to Maintain Weight According to Height?
The height to weight ratio chart can help you identify whether your weight is healthy. The next step is to maintain a healthy weight if you are underweight or overweight. Remember that achieving a zero figure size is often unrealistic and has great restrictions. Always look for maintaining an ideal weight, which benefits overall health and well-being. Here are some effective tips to help you achieve and sustain your ideal weight:
- Eat a Healthy and balanced diet
- Calculate your calroie needs
- If needed, create a calorie deficit
- Regularly Exercise
- Hydrate Yourself
- Take Adequate Rest
1. Eat a Healthy and Balanced Diet
Eating a healthy and balanced diet involves selecting the right foods and paying attention to portion sizes and meal timings. It’s essential to include a variety of colourful fruits and vegetables to ensure a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Incorporating lean proteins like poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes helps support muscle growth and repair. Whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats provide complex carbohydrates for sustained energy levels. Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are vital for heart health and nutrient absorption. Moreover, you can follow meal plans or try a keto diet plan for specific health goals.
2. Calculate Your Calorie Needs
Calculating your calorie needs involves considering factors beyond basal metabolic rate, such as physical activity level, age, height, weight, and individual goals. Tools like online calculators or consulting with a nutritionist can help you understand the daily calorie intake. Additionally, keeping a food diary or using mobile apps can aid in tracking food consumption, allowing for better awareness of calorie intake and adjustments as needed to meet specific health or fitness goals.
3. If Needed, Create a Calorie Deficit
Creating a calorie deficit for weight loss should be done gradually and safely. This can be achieved by reducing portion sizes, choosing lower-calorie alternatives, increasing physical activity levels, or a combination of these strategies. It’s crucial to prioritise nutrient-dense foods to ensure that essential vitamins and minerals are still consumed, even while reducing overall calorie intake.
4. Engage in Regular Exercise
Engaging in various exercises, including cardiovascular, strength training, flexibility, and balance exercises, helps promote overall fitness and well-being. Finding activities you enjoy and making them a regular part of your schedule increases your chances of staying in your workout. Additionally, mixing up your workouts prevents boredom, reduces the risk of overuse injuries, and ensures that different muscle groups are targeted. Setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) fitness goals can provide motivation and direction for your exercise plan.
5. Hydrate Yourself
In addition to water, consuming hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables can contribute to overall hydration levels. Monitoring hydration status, especially during hot weather, intense physical activity, or illness, and adjusting fluid intake accordingly is essential. Electrolyte-rich beverages like coconut water or sports drinks may benefit rehydration after long exercise sessions.
6. Take Adequate Rest
Prioritising relaxation and stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or gentle yoga, can promote better sleep quality and overall well-being. Creating a comfortable sleep environment, including a calm, dark, and quiet bedroom, and establishing a consistent sleep schedule can help regulate your body’s internal clock and improve sleep hygiene. Additionally, limiting screen time before bedtime and, avoiding caffeine and stimulating activities in the evening can support a more restful sleep.
Major Factors that Affect Height and Weight
A combination of factors, including diet, lifestyle, genetics, and environmental factors, influences weight. Here are some of the key factors that can affect height and weight:
1. Diet: The type and quantity of food you consume are crucial in weight management. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can support weight loss or maintenance. On the other hand, excessive consumption of sugary, high-calorie, and processed foods can lead to weight gain.
2. Physical Activity: Regular physical activity helps burn calories and improves overall fitness. Engaging in aerobic exercises, strength training, and other forms of physical activity can aid in weight loss and maintenance. An ideal weight calculator can assist you in determining a healthy weight range based on your height, providing a helpful reference for maintaining the level of physical activity essential for well-being.
3. Metabolism: Metabolism refers to the rate at which your body burns calories to produce energy. Metabolic rate can be influenced by age, sex, muscle mass, and genetics. Individuals with a higher metabolic rate tend to burn more calories even at rest.
4. Genetics: Genetic factors can influence how your body stores and processes fat. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to gain weight more easily than others, even with similar dietary and activity levels.
5. Hormones: Hormones play a significant role in regulating appetite, metabolism, and fat storage. Hormonal imbalances, such as insulin resistance or thyroid disorders, can impact weight management. Consider using a height weight chart for females and males to understand your target weight range for optimal health.
6. Stress: Chronic stress can lead to emotional eating and affect hormone levels, which may contribute to weight gain. Finding healthy ways to manage stress is essential for weight management.
7. Sleep: Inadequate sleep can disrupt hormonal balance and increase cravings for unhealthy foods, leading to weight gain. Quality sleep is crucial for overall health and weight management.
Impact of Being Overweight
Being overweight not only affects physical appearance but also affects health and well-being in the long term. The impact of excess weight extends into various aspects of life, including physical health, mental well-being, and social dynamics. Research suggests that If you have too much weight, especially around your waist, you’re more likely to have health issues. Here’s an overview of the impacts of being overweight:
- Heart Diseases
- Risks of Diabetes
- Chances of Stroke
- Increased Risk of Cancer
Let us discuss these in detail-
1. Heart Diseases
When you carry extra weight, your heart must pump harder to supply blood to all body parts. This extra effort can lead to conditions like high blood pressure, where the force of blood against your artery walls is consistently too high. High cholesterol, another risk factor, occurs when there’s too much fat in your blood, which can clog arteries and lead to heart disease. Ultimately, this can increase the chances of having a heart attack or developing other heart-related issues.
2. Risks of Diabetes
Being overweight can make your body less sensitive to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. This can result in insulin resistance, where your body doesn’t respond to insulin properly. Over time, this can lead to type 2 diabetes, where your blood sugar levels become consistently high. Diabetes can cause various health problems, including nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems.
3. Chances of Stroke
Strokes occur when there’s a problem with blood flow to the brain, and it can cause permanent brain damage or even be fatal, depending on the severity and location. When someone is overweight or obese, they are more likely to develop conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which increase the risk of strokes. Excess weight can contribute to the buildup of plaque in your arteries, a condition called atherosclerosis. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, and other substances that can narrow and harden your arteries, restricting blood flow to vital organs like the brain. If a blood clot forms and blocks a narrowed artery in the brain, it can result in a stroke.
4. Increased Risk of Cancer
Carrying extra weight, especially around the waist, can lead to long term low-grade inflammation in the body. This inflammation can promote the growth of cancer cells and increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Additionally, fat cells can produce hormones and other substances that may encourage cancer growth. Common cancers associated with obesity include breast cancer (in postmenopausal women), colorectal cancer, kidney cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
Expert Review on Height Weight Chart
Height weight charts are an in-depth analysis of the correlation between an individual’s height and weight, typically using Body Mass Index (BMI) as a key metric. These charts serve as a valuable resource for assessing whether a person falls within a healthy weight range based on their height. Experts evaluate the charts for accuracy in reflecting population health trends, identifying potential health risks associated with underweight or obesity, and informing recommendations for balanced lifestyles. Continuous scrutiny and updates to these charts are essential to ensure they align with current health standards and provide reliable guidance for individuals and healthcare professionals.
References
- n.d. Wikipedia. Accessed May 4, 2024. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274736065_A_Scientific_Approach_to_Being_All_About_That_Bass/figures?lo=1
- “Assessing Your Weight | Healthy Weight, Nutrition, and Physical Activity | CDC.” n.d. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed May 4, 2024
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/index.html
- Ben-Joseph, Elana P. n.d. “Growth Charts (for Parents) | Nemours KidsHealth.” Kids Health.
- Accessed May 4, 2024. https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/growth-charts.html
- “Body Mass Index Table.” n.d. NHLBI. Accessed May 4, 2024. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/BMI/bmi_tbl.pdf
- “Calculate your body mass index (BMI) – NHS.” n.d. NHS. Accessed May 4, 2024. https://www.nhs.uk/health-assessment-tools/calculate-your-body-mass-index/
- “Comparison of ideal body weight equations and published height weight tables with body mass index tables for healthy adults in the United States.” n.d. PubMed. Accessed May 4, 2024. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16772549/
- Mascherini, Gabriele. n.d. “Growth Charts for Height, Weight, and BMI (6–18 y) for the Tuscany Youth Sports Population.” MDPI. Accessed May 4, 2024. https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/16/24/4975
- “Measuring Children’s Height and Weight Accurately At Home | Healthy Weight, Nutrition, and Physical Activity | CDC.” n.d. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed May 4, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/childrens_bmi/measuring_children.html.
FAQs
What is the weight and height according to age?
Height to Weight ratio chart is the range of weights and heights expected for individuals at different stages of their development, usually measured in relation to their age. This information is often represented in growth charts, which help track the growth and development of children over time. These charts provide general guidelines for what is considered typical or average for a particular age group, although individual variations are common.
What is the weight for 5.2 height?
The weight for someone who is 5.2 inches tall shall be between 44.9 to 54.9 kgs for women and 51.7 to 68 kgs for men. This weight may vary based on age, gender, body composition, and overall health. These ranges can vary, and it’s essential to consider factors such as muscle mass and body composition when determining a healthy weight. Consulting with a healthcare provider can provide personalised guidance.
What is a good weight for my height?
To understand what a good weight should be for your height, you must know the ideal BMI for your height category. Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. It’s commonly used to assess whether an individual’s weight falls within a healthy range for their height. However, it’s important to note that BMI is a general indicator and may not account for factors such as muscle mass or body composition. Here’s the ideal weight ranges suggested by the National Institute of Health (NIH):
| Height (Feet-Inches) | Ideal Weight Range (Kilograms) |
|---|---|
| 4’10” – 5’0″ | 41 – 56 |
| 5’1″ – 5’3″ | 45 – 61 |
| 5’4″ – 5’6″ | 50 – 67 |
| 5’7″ – 5’9″ | 55 – 73 |
| 5’10” – 6’0″ | 60 – 80 |
| 6’1″ – 6’3″ | 66 – 87 |
| 6’4″ – 6’5″ | 71 – 91 |
What is the correct height and weight kg?
The correct height and weight for an individual can vary depending on various factors such as age, body composition, muscle mass, and overall health. However, one common metric used to assess healthy weight is the Body Mass Index (BMI), which calculates an individual’s body fat based on height and weight. BMI calculations suggests:
- Ideal body weight (men) = 50 kg + 1.9 kg for every inch above 5 feet
- Ideal body weight (women) = 49 kg + 1.7 kg for every inch above 5 feet
What is the correct weight according to age?
The correct weight according to age varies depending on factors like height, body composition, and overall health. Generally, a healthy weight for a specific age can be determined by referencing growth charts or BMI ranges for that age group. These charts provide a range of weights that are considered for individuals of different ages.
What is correct height and weight?
To find your height, stand straight against a wall and measure from the floor to the top of your head. For weight, stand on a scale without shoes and record the number. Then, use tools like BMI calculators to see if your measurements are within a healthy range for your age and gender. Here are the BMI ranges from researches:
- If your BMI is less than 18.5, it falls within the underweight range.
- If your BMI is 18.5 to 24.9, it falls within the Healthy Weight range.
- If your BMI is 25.0 to 29.9, it falls within the overweight range.
- If your BMI is 30.0 or higher, it falls within the obese range.
How do you calculate weight per age?
To calculate weight per age, you look at charts that show the average weight for people of different ages. These charts give you an idea of what’s normal for someone of a certain age. It’s like a guide to see if someone’s weight is where it should be for their age. Follow these steps:
- Refer to a Growth Chart, maybe suggested by a doctor
- Locate Age and Gender
- Check Weight Range
- Compare
What is a Normal Weight?
A normal weight is considered to fall within the “Healthy Weight” range on the BMI scale suggested by the CDC, which is between 18.5 and 24.9. If your BMI falls within this range, your weight is generally considered healthy for your height.