How To Get Diagnosed For Thyroid: Tests & Tips. This article lists tips and tests that a person can do to understand their thyroid function
Thyroid tests are used by doctors to determine how well your thyroid is working and to determine the cause of problems such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in your neck that produces two thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) (T3). Thyroid hormones regulate how the body uses energy, so they affect nearly every organ, including the heart.
Thyroid tests assist doctors in diagnosing thyroid diseases such as
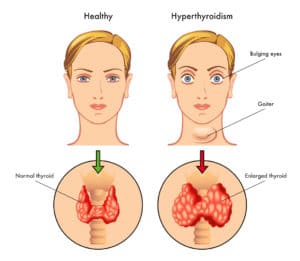
- Hyperthyroidism occurs when thyroid hormone levels are abnormally high.
- The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease.
- Hypothyroidism occurs when thyroid hormone levels are abnormally low.
- The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s disease.
Blood Tests to check for Thyroid Function
-
TSH test
TSH levels in the blood are usually checked first by medical professionals. It is a pituitary hormone that tells the thyroid how much T4 and T3 to produce.
A high TSH level usually indicates hypothyroidism or an underactive thyroid. This indicates that your thyroid isn’t producing enough hormones. As a result, the pituitary gland continues to produce and release TSH into your bloodstream.
A low TSH level typically indicates hyperthyroidism or an overactive thyroid. Because your thyroid produces too much hormone, the pituitary gland stops producing and releasing TSH into your blood.
If the test results are abnormal, you will need at least one other test to help determine the cause of the problem.
-
T4 tests
A high level in the blood may indicate hyperthyroidism. A low T4 level could indicate hypothyroidism.
In some cases, having high or low T4 levels does not necessarily indicate that you have thyroid problems. Thyroid hormone levels will be higher if you are pregnant or taking oral contraceptives NIH external link. T4 levels can be reduced by severe illness or the use of corticosteroids (medicines used to treat asthma, arthritis, skin conditions, and other health issues). These conditions and medications alter the number of proteins in your blood that “bind” to T4. T4 is bound and stored in the blood until it is needed. T4 that is not bound to these proteins is free to enter body tissues. Many healthcare professionals prefer to measure free T4 levels because they have an effect on them.
If the test results are abnormal, you will need to perform at least one additional test to determine the source of the problem.
-
T3 test
If your doctor suspects you have hyperthyroidism despite having a normal T4 level, you may be given a T3 test to confirm the diagnosis. When T4 is normal but T3 is high, measuring both T4 and T3 levels can help to diagnose hyperthyroidism.
-
Thyroid antibody tests
Antibody levels may aid in the diagnosis of an autoimmune thyroid disorder such as Graves’ disease (the most common cause of hyperthyroidism) or Hashimoto’s disease (the most common cause of hypothyroidism). Thyroid antibodies are produced when your immune system incorrectly attacks the thyroid gland. If the results of other blood tests indicate thyroid disease, your doctor may order thyroid antibody tests.
Imaging Tests for Thyroid Disease
Ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound is most commonly used to detect or examine thyroid nodules. Thyroid nodules are lumps found in the neck. Your doctor can use ultrasound to determine whether the nodules are cancerous.
You will lie on an exam table for an ultrasound, and a technician will run a device called a transducer over your neck. The transducer uses sound waves that bounce off your neck to create images of your thyroid. The ultrasound usually lasts 30 minutes.
Thyroid scan
A thyroid scan is used by doctors to examine the size, shape, and position of the thyroid gland. This test employs a small amount of radioactive iodine to aid in the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism and the detection of thyroid nodules. For a week before the test, your doctor may advise you to avoid foods high in iodine, such as kelp, or medicines containing iodine.
A technician injects a small amount of radioactive iodine or a similar substance into your vein for the scan. You can also take the substance as a liquid or capsule. The scan is performed 30 minutes after injection or up to 24 hours after you swallow the substance to allow your thyroid time to absorb it.
During the scan, you will be lying on an exam table while a special camera photographs your thyroid. The scan usually takes no more than 30 minutes.
Thyroid nodules that produce an excessive amount of thyroid hormone are clearly visible in the images. The presence of radioactive iodine throughout the thyroid could indicate Graves’ disease.
Even though a thyroid scan requires only a small amount of radiation and is thought to be safe, you should not have this test if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.