A lot of people these days suffer from high blood sugar and don’t know how to control diabetes and how to control sugar level immediately. Reasons such as an unhealthy diet, stress, and no exercise are to blame. Chronic high blood sugar is also known as Diabetes. In this condition, your body is unable to produce insulin which helps the body to regulate blood sugar levels. This leads to a spike in blood sugar levels in your body. Diabetes can be a really dangerous disease if not controlled. Untreated Diabetes can lead to kidney failure and even blindness. Therefore, it becomes really important to know how to control diabetes and how to control sugar level immediately.
People often do not know how to control diabetes and how to reduce blood sugar level immediately. This leads to the worsening of the condition as people go about eating whatever they can lay their hands on without realizing that it can be damaging to their bodies. Before knowing how to control sugar a person must know what caused it in the first place so they can be aware of what to avoid to reduce the chances of their condition worsening. Diabetes is of two types. Type 1 and Type 2. Diabetes Type 1 is genetic and Type 2 is caused by an unhealthy lifestyle. This blog will tell you how to control diabetes and how to reduce blood sugar level immediately.
How can I check my Blood Sugar
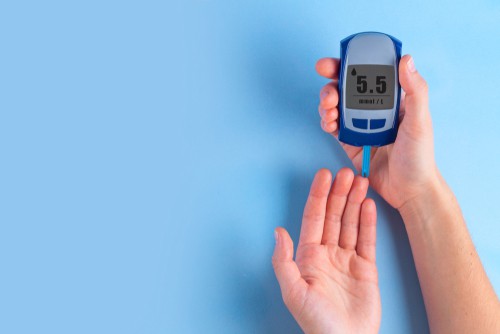
If you want to know how to control diabetes or how to reduce blood sugar level immediately then checking your blood sugar is vital when you are suffering from diabetes. It tells you how high is your blood sugar levels and can give you an idea about how to control diabetes more effectively and can help you to know how to control sugar level immediately In order to check your blood sugar levels you need to use a blood glucose monitor. Here’s how you can check your blood sugar levels
Step 1: Always make sure that the blood glucose monitor is clean before use.
Step 2: Now take out one of the test strips which came with your blood glucose monitor and insert it in the machine.
Step 3: The next step would be to wash your hands with soap and water. This will ensure that your hands are clean.
Step 4: Using the lancet, prick the upper edge of your finger and squeeze lightly to ensure the blood comes out.
Step 5: Now gently touch the test strip with your finger, dropping some blood on it.
Step 6: Now wait for a few seconds and your blood sugar level will be displayed on the screen.
Step 7: Dispose of the test strip, use a new test strip every time your measure your blood sugar levels.
If your blood sugar levels are high and you want to know how to reduce blood sugar level immediately then the best thing you can do is to consult your doctor.
When should I check my Blood Sugar
If you are struggling to know how to control diabetes and how to reduce blood sugar level immediately then checking your blood sugar levels at the right time can make a lot of difference. The right time to check blood sugar levels will vary from person to person. A person with a severe case of Diabetes may need to check their blood sugar levels constantly throughout the day to better manage their conditions. On the other hand, a person with mild diabetes may only need to check their blood sugar levels once or twice a day. Usually, blood sugar levels are checked early in the morning before meals and at bedtime. If you have high blood sugar levels and and do not know how to control diabetes. Your doctor will suggest you the right time to check your blood sugar levels. Also if you want to know how to control sugar level immediately then some home remedies like neem and jamun seeds can help.
How should I get tested for Diabetes
If you are experiencing symptoms of diabetes then there are a lot of tests that can determine if you have Diabetes or not. These tests will help you to know about your blood sugar levels and also give you an idea about how to control diabetes and will also give you an idea about how to control sugar level immediately. Being aware about and getting tested early can also help you with how to reduce blood sugar level immediately.
1. HbA1c test
For people who do not know how to control diabetes. They can try this test. It is a nonfasting blood test. This test will tell you your average blood sugar levels for the past 2-3 months. This test does not require any preparation. Unlike the finger prick test done on a blood glucose monitor, this test involves taking a professional taking blood from your vein. The results of this test will indicate in what range your blood sugar levels were for the past 2-3 months. Depending on the reports, your healthcare professional will tell you if you have Diabetes or not. These diabetes products can help you a lot.
2. Random Blood Glucose Test
This test is done any time of the day. You can either have it done in a finger-prick way or by taking blood from your veins. This test indicates your random blood sugar levels. A random blood glucose test can also help you with how to reduce blood sugar level immediately. You can take the right action on time if your blood sugar levels are too high.
3. Fasting Blood Glucose Test
In this test, fasting is required for eight hours. You do not have to eat or drink anything during those eight hours. This is to avoid any interference with the results. This test is done in the morning. A lot of people have high fasting glucose can do not know how to control sugar level immediately. Try out these diabexey products to better control your blood sugar levels.
How to reduce blood sugar level immediately?
If you don’t know how to control diabetes or how to reduce blood sugar level immediately then not controlling your blood sugar levels can cause a lot of issues in the long run. It is always ideal to act on your high blood glucose immediately to avoid any further complications. Here are some ways in which you can reduce your blood sugar levels immediately.
1. Taking Insulin can help in reducing the blood sugar levels in your body. Insulin helps blood sugar to enter the body’s cells to be used as fuel. Taking insulin injections can help to reduce the blood sugar levels in the body immediately and help you with your issue of how to control sugar level immediately. If you are struggling to control your blood sugar levels then here are some diabetes plans that can help you with it.
2. Exercising is the best solution to your question of how to control diabetes. It can also help to bring down your blood glucose levels immediately. It is the best way to reduce your blood sugar levels without any medication. Doing exercise utilizes the blood sugar present in your body for energy and can help you to know how to control sugar level immediately
3. Drinking water can also help in reducing blood sugar levels. It may not be the fastest way but drinking water can enable your kidneys to flush out excess sugar present in your body through urine and can help you to know how to control sugar level immediately
4. Taking your medications on time and never missing a dose can also help you to regulate blood sugar levels. A lot of times people miss their dose which causes high blood sugar in the body. People often skip their medications and then rely on other resorts to know how to control sugar level immediately
Home Remedies to reduce sugar level
People these days do not know how to control diabetes in a proper way. There are numerous remedies available at your very own home that can help you regulate and manage your blood sugar levels and help you with how to reduce blood sugar level immediately.
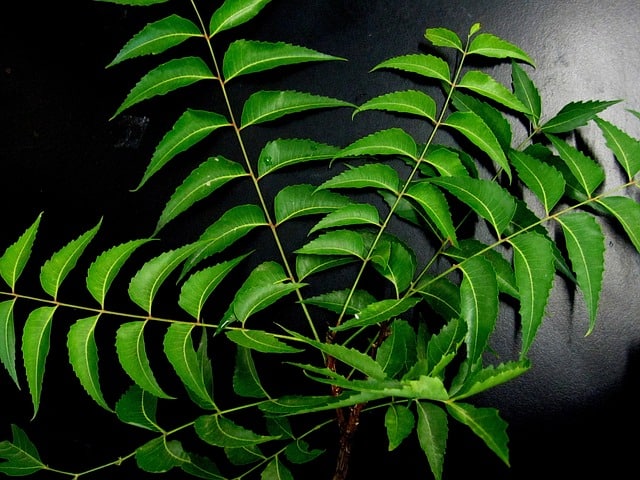
1. Neem
Neem is really effective against Diabates. It contains various antiviral substances and glycosides that help to control your blood sugar levels. You can make neem powder at home by blending neem leaves. You can drink it with water once or twice a day. Drinking Neem water is a great solution to the problem of how to control sugar level immediately
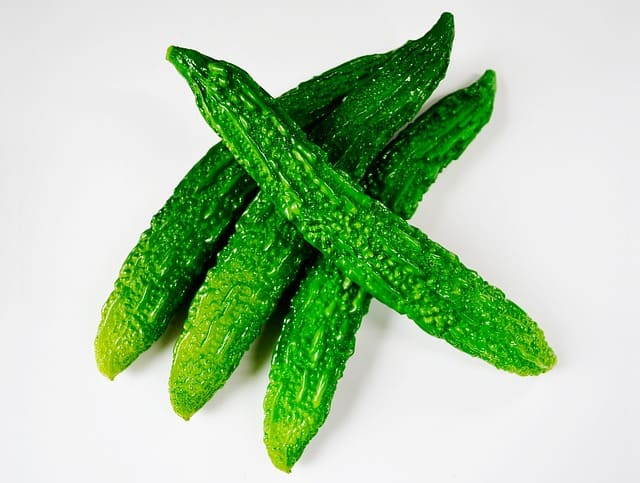
2. Karela
There are two substances found in Karela that help to reduce blood sugar levels. These are Charatin and Momordicin. Having a glass of Karela can bring down your blood sugar levels and help you to manage your Diabetes. Having Karela juice can be your answer to how to control diabetes and how to control sugar level immediately or how to reduce blood sugar level immediately
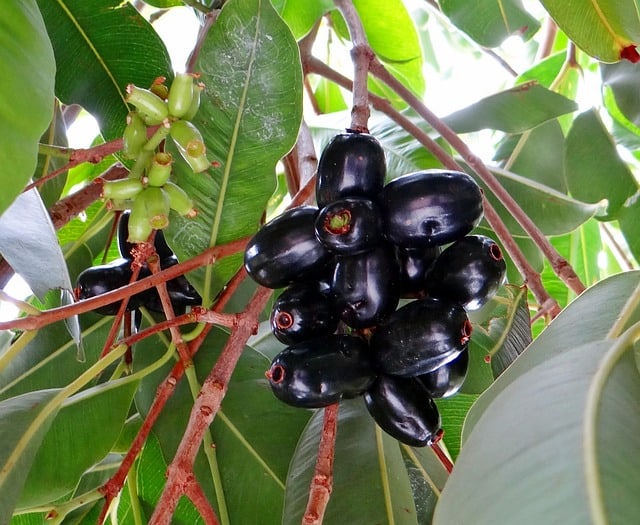
3. Jamun
Jamun seeds are bitter in taste and are really effective in controlling blood sugar levels. You can make a powder out of Jamun seeds and drink it with water for the best results and know how to to control sugar level immediately or how to reduce blood sugar level immediately.
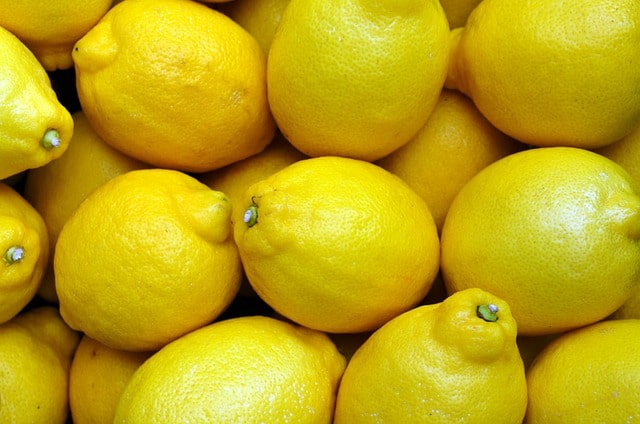
4. Lemon
A simple lemon can be your solution to how to control diabetes and how to control sugar level immediately. Lemon can help you to manage your blood sugar levels and lower insulin resistance. Having a glass of lemonade without any added sugar can help you to better manage your blood sugar levels.
What else can I do to help manage my Diabetes?
A lot of people are confused regarding how to control diabetes and how to control sugar level immediately and it’s a valid worry because managing diabetes can be really hard but it can be made easy if you are aware of foods that can help you manage it. Consuming foods rich in Vitamin D can help you to manage your diabetes a lot better. Foods and drinks like eggs, milk, fatty fish and can help you to manage your blood sugar levels a lot better. According to a study intake of Vitamin D was associated with a lower risk of insulin resistance. Taking Vitamin D daily will also help keep your bones and teeth healthy and also help you with how to control blood sugar.
How can I control Diabetes with lifestyle changes?
Making certain lifestyle changes can help you to regulate blood sugar levels in your body. People who suffer from Diabetes don’t know how to how to reduce blood sugar level immediately even when there are a lot of home remedies available at home that can help you to do so.
1. Exercise
Exercise is one of the best ways to know how to control blood sugar. When you exercise your body uses glucose as a source of energy. This helps to control and regulate your blood sugar levels as your muscles need an energy source to perform any task.
2. Eating Healthy
A lot of people don’t know how to how to control blood sugar by eating healthy. Eating healthy is one of the best ways and the answer to the question of how to reduce blood sugar level immediately. What you eat will decide how your body performs and functions. A diet high in refined carbs and sugar will raise your blood sugar levels and can put you at risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes. On the other hand, eating foods rich in fiber can help regulate blood sugar in your body as fiber makes you feel fuller for longer reducing any hunger pangs.
3. Keeping track of your blood sugar levels
This is by far the most skipped step when it comes to how to reduce blood sugar level immediately. Keeping track of your blood sugar levels from time to time can help you to manage your blood sugar levels a lot better. This will help you to exercise and eat healthily when required and also help you to know how to reduce blood sugar level immediately
4. Trying out home remedies.
A lot of people at home do not know how to how to reduce blood sugar level immediately or how to control blood sugar. There are a lot of home remedies that can help you with it. Drinking lemon water and Karela Juice can help bring down your blood sugar levels. This is due to the presence of certain substances in them that helps to metabolize sugar. Check out some amazing diabetes recipes
5. Do not skip your medications
A lot of people skip medications and then don’t know how to reduce blood sugar level immediately. Skipping medications can make your blood sugar levels go up. The very thing you can do to deal with this issue is to not skip your medications. Consult your doctor incase of a skipped medication.
The Bottom Line
Figuring out how to control diabetes can be a challenge. Having high blood sugar levels in the body for a long time is a sign of Diabetes. In this condition, the body is unable to utilize the insulin which leads to a rise in blood sugar levels in the body. If you are experiencing signs and symptoms of diabetes then it is in your best interest to get tested. There are various tests to determine if you have diabetes or not such as HbA1c, random blood glucose test, and fasting blood glucose test which will tell you your sugar levels and also give you an idea about how to control diabetes. Read more diabetes blogs here.
Various home remedies such as Neem, Karela, and Lemon can help you to control your blood sugar levels. Consuming foods rich in Vitamin D can also help reduce the chances of developing diabetes.
FAQ’s
What is the best way to control diabetes?
The best way to control diabetes is to live a healthy lifestyle. Eating healthy and being physically fit will reduce your dependency on medications.
Which food helps to reduce Diabetes?
Foods such as leafy greens, seafood, eggs, and nuts can really help you to control your blood sugar levels.
Can I control diabetes myself?
With the right diet and exercise anyone can control diabetes.
How to control blood sugar immediately?
You can control blood sugar levels immediately by using insulin injections, drinking more water, and exercising.
How to control Diabetes with healthy food?
Diabetes can be controlled with a healthy diet. A diet rich in leafy greens, low carbs, and protein can help you to manage your blood sugar levels.
How to control Diabetes without medications?
You can control Diabetes without medications by following a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a healthy diet and exercising daily.
How to control Diabetes with homemade recipes?
You can make recipes that are low in carbs and high in fiber and protein. Fiber disgests slowly in your body and makes you feel fuller for longer.
how to reduce blood sugar level immediately at home?
A lot of people struggle to know how to reduce blood sugar level immediately at home. There are a lot of home remedies like Karela juice and lemon water which can help you to bring your blood sugar levels down.