Your friend eats whatever she wants and stays slim. You gain weight from just looking at food. Everyone tells you it’s genetics or age, but you’re desperate for solutions. The truth? Your metabolic rate isn’t fixed destiny. While genetics play a role, specific science-backed strategies can increase metabolism significantly. Understanding how to boost metabolism empowers you to burn more calories naturally, making weight loss easier without extreme dieting. This guide reveals proven methods that work for Indian bodies and lifestyles, not just imported advice that ignores our reality.
What Is How To Boost Metabolism and Why Indian Dieters Should Care?
Metabolism is the sum of all chemical processes your body uses to convert food into energy and maintain life. How to boost metabolism means increasing the rate at which your body burns calories at rest, during activity, and when digesting food. Your metabolic rate has three components: basal metabolic rate (BMR) covering basic functions, non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT) for daily movement, and thermic effect of food (TEF) for digestion. Additionally, exercise adds extra calorie burn. Boosting any component increases metabolism overall. While genetics determine baseline, lifestyle choices significantly influence how fast or slow your metabolism runs. Therefore, you’re not a helpless victim to slow metabolism but can actively improve it through strategic changes in eating, movement, and lifestyle habits.
Why How Matters for Indian Bodies
Indians face specific metabolic challenges, making how to boost metabolism especially important. Research shows Indians havea 3 to 5% lower metabolic rate than other populations at similar body weights.
Additionally, we have higher body fat percentages and lower muscle mass at the same BMI. Since muscle burns more calories than fat, this genetic predisposition means lower calorie burn. Moreover, traditional Indian diets heavy in carbs can promote insulin resistance, which further slows metabolism.
Urban Indian lifestyles with extreme sedentary behavior drastically reduce NEAT. In fact, sitting 10+ hours daily can reduce daily calorie burn by 300 to 400 calories compared to more active living. Furthermore, chronic stress is common among urban professionals, which elevates cortisol, promoting muscle breakdown and slowing metabolism. Understanding these population-specific factors helps address how to boost metabolism effectively rather than following generic advice that ignores Indian reality.
Common Myths Debunked About This Topic
Let’s clear up dangerous myths about how to boost metabolism. First, eating every 2 hours doesn’t significantly boost metabolism. Total daily intake matters more than frequency. Second, metabolism doesn’t “shut down” if you skip breakfast. Meal timing is flexible. Third, spicy foods and green tea have minimal metabolic effects, burning maybe 10 to 20 extra calories daily. Don’t expect miracles from metabolism boosting foods alone. Fourth, metabolism doesn’t drastically slow with age. The decrease is primarily from muscle loss and reduced activity, both preventable. Additionally, very low-calorie diets don’t permanently damage metabolism, though they slow it significantly during and after dieting. Finally, you can’t target belly fat through metabolism tricks. Fat loss happens proportionally across your body based on genetics. Therefore, focus on proven strategies like building muscle and staying active rather than gimmicks promising easy fixes.
The Science Behind How To Boost Metabolism for Indians
How How Works in Your Body
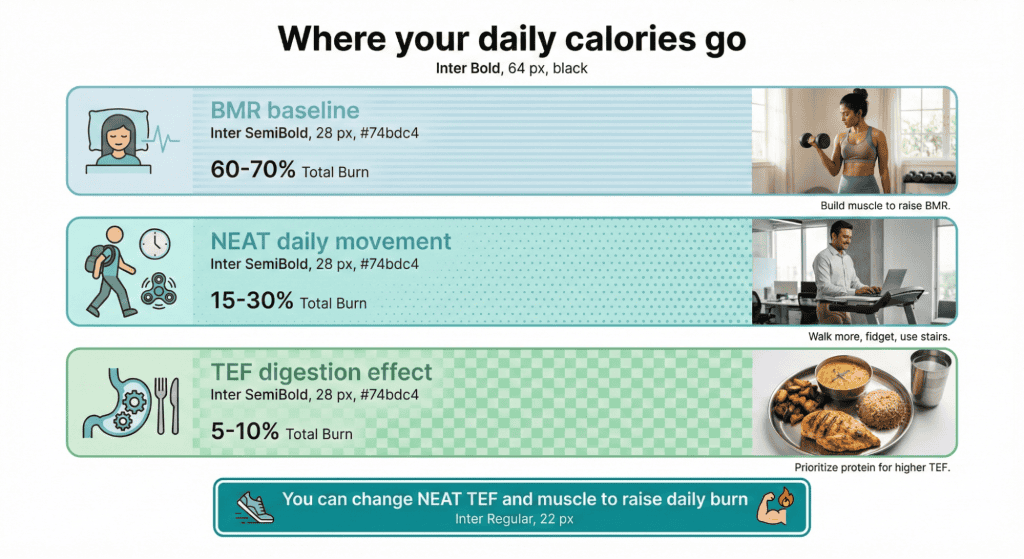
Your body burns calories 24/7 through multiple mechanisms you can influence. BMR accounts for 60 to 75% of total daily burn, covering essential functions like circulation, breathing, and cell production. Additionally, muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue, approximately 6 calories per pound daily versus 2 for fat.
Therefore, building muscle increases metabolism permanently. NEAT contributes 15 to 30% of daily burn through all non-exercise movement like walking, fidgeting, and maintaining posture. Moreover, TEF uses 10 to 15% of calories consumed to digest food, with protein having the highest thermic effect at 20 to 30% versus 5 to 10% for carbs and 0 to 3% for fats.
Exercise adds variable amounts depending on intensity and duration. Understanding these components shows how to boost metabolism through multiple pathways: building muscle, increasing daily movement, eating adequate protein, and staying active rather than relying on single magic bullets.
The Connection Between Increased Metabolism and Health
Increasing metabolism creates benefits beyond just easier weight loss. A higher metabolic rate means more energy throughout the day, reducing chronic fatigue. Additionally, better glucose control results as improved insulin sensitivity accompanies higher metabolism. This reduces diabetes risk significantly.
Moreover, increased muscle mass from thermogenesis strategies supports bone density, reducing osteoporosis risk, particularly relevant for Indian women. Better metabolic health improves cholesterol profiles, lowering heart disease risk. In fact, research shows higher metabolism correlates with longevity and healthspan. People with faster metabolism tend to age better physically and maintain independence longer.
Furthermore, the lifestyle changes that boost metabolism like strength training and adequate protein improve mood, sleep quality, and stress resilience. Therefore, pursuing higher metabolic rate isn’t just about vanity or weight but comprehensive health improvement affecting every aspect of wellbeing.
What Research Shows for Indian Population
Research on metabolism in Indians reveals concerning but actionable patterns. Studies show Indians develop insulin resistance and diabetes at younger ages and lower BMIs than other populations, partly due to lower metabolic rate. One study found that Indians burn approximately 200 fewer calories daily than Europeans at the same body weight.
Additionally, research indicates that Indians lose muscle mass more easily during weight loss diets, further reducing metabolic rate. Moreover, studies on thermogenesis show that Indians may have reduced brown adipose tissue activity, which generates heat and burns calories.
However, research also demonstrates that resistance training improves metabolic rate in Indians just as effectively as in other populations, and increasing protein intake significantly helps preserve muscle during weight loss. Therefore, while genetic factors create challenges, the same metabolism boosting strategies work when applied consistently.
Metabolic Rate: What to Watch For
Physical Signs and Symptoms to Monitor
Your metabolic rate manifests through observable signs you can track. High energy levels throughout the day without afternoon crashes indicate healthy metabolism. Additionally, feeling comfortably warm in normal temperatures shows your body generating adequate heat from metabolic processes. Strong athletic performance and quick recovery from exercise signals efficient energy production.
Moreover, maintaining stable weight while eating adequate calories demonstrates balanced metabolic rate. Conversely, symptoms of slow metabolism include constant fatigue despite adequate sleep, feeling cold especially hands and feet, difficulty losing weight despite low calories, slow recovery from exercise, and brain fog. Watch for thinning hair, brittle nails, and dry skin as these indicate inadequate energy production.
Furthermore, bloating and constipation can signal slow digestion, a component of overall metabolism. Tracking these signs helps you assess whether metabolism boosting strategies are working beyond just scale weight.
Emotional and Mental Health Indicators
Metabolic rate profoundly affects mental health through brain energy supply. Healthy metabolism supports stable mood, motivation, and mental clarity. Your brain uses 20% of total calorie burn despite being only 2% of body weight. Additionally, adequate energy production supports neurotransmitter synthesis for mood regulation.
Therefore, slow metabolism often manifests as depression, anxiety, and irritability from inadequate brain fuel. Moreover, motivation and willpower depend heavily on having adequate energy. When metabolism is sluggish, you lack drive to exercise, meal prep, or pursue goals. In fact, many people blame laziness or lack of discipline when the real issue is inadequate metabolic energy production.
Furthermore, sleep quality depends on metabolic health. Poor metabolism disrupts sleep hormones, creating vicious cycles. Improving metabolic rate through proper strategies often dramatically enhances mental health, motivation, and sleep before weight changes become visible.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
See a doctor if you have severe fatigue interfering with daily activities despite adequate sleep and nutrition. Consult a healthcare professional for unexplained weight gain while eating normally and exercising regularly. Additionally, get tested if you experience cold intolerance, hair loss, dry skin, constipation, or menstrual irregularities, as these might indicate thyroid dysfunction rather than just slow metabolism from lifestyle.
Moreover, if you’re doing everything right with diet, exercise, and sleep but still struggling with energy and weight, underlying medical conditions like hypothyroidism, PCOS, or insulin resistance might need treatment.
Furthermore, work with a registered dietitian if you’ve tried extreme diets that damaged your metabolism, requiring professional guidance for recovery. Don’t self-diagnose or treat serious metabolic disorders with supplements or diet changes alone. Blood tests can reveal issues requiring medical intervention beyond lifestyle modifications.
Indian Lifestyle Factors Affecting How To Boost Metabolism
Modern Indian Diet Challenges and Solutions
Modern Indian eating patterns inadvertently slow metabolism through several mechanisms. Skipping breakfast then overeating at dinner disrupts metabolic rhythms and promotes fat storage. Additionally, carb-heavy diets without adequate protein fail to preserve muscle during weight loss, reducing metabolic rate progressively.
Moreover, ultra-processed foods with refined flour and sugar cause insulin spikes and crashes, eventually promoting insulin resistance that slows metabolism. In fact, the lack of fiber from eating white rice instead of brown rice, refined wheat instead of whole grains, reduces satiety and gut health, both affecting metabolic efficiency. Solutions include eating protein at every meal to preserve muscle and leverage high TEF. Choose whole grains over refined.
Additionally, include vegetables at lunch and dinner for fiber and nutrients. Don’t skip meals or eat erratically. Consistent eating patterns support a stable metabolic rate better than irregular patterns creating metabolic confusion.
Work-Life Balance and Urban Living Impact
Urban Indian professional life creates metabolic slowdown through extreme sedentary behavior. Sitting for 10+ hours daily dramatically reduces NEAT, dropping daily calorie burn by 300 to 400 calories. Additionally, taking elevators, driving short distances, and having minimal physical household duties eliminate incidental activity that historically kept metabolism higher.
Moreover, work stress elevates cortisol chronically, promoting muscle breakdown and abdominal fat storage while slowing metabolic rate. Lack of sleep from long commutes and work demands disrupts metabolic hormones, particularly leptin and growth hormone.
Furthermore, reliance on food delivery and restaurants means eating at unpredictable times with poor nutritional quality. In fact, air pollution affects mitochondrial function, potentially reducing cellular energy production. Address these by taking movement breaks every hour at work. Stand during some meetings. Park farther away. Take stairs. Prioritize 7 to 8 hours of sleep as non-negotiable. These changes boost metabolism by increasing NEAT and optimizing hormonal environment.
Cultural and Social Influences on Health
Indian culture both supports and hinders efforts to increase metabolism. Traditional physically active lifestyles and home cooking supported higher metabolic rate naturally. However, modern aspirations toward sedentary white-collar work and status-signaling through car ownership reduce activity. Additionally, social eating events centered on carb and fat-heavy foods make it difficult to eat adequately protein-rich meals.
Moreover, gym culture focuses excessively on cardio while neglecting strength training essential for building metabolism-boosting muscle. In fact, cultural body image preferences sometimes discourage women from strength training due to fear of looking “bulky.” Family dynamics might pressure you to eat certain foods or amounts regardless of your metabolic needs. Navigate these by educating family about protein importance. Choose strength training despite cultural discomfort. Walk or bike for some errands rather than always driving. Bring protein-rich options to social events. These choices honor metabolic health while navigating cultural realities.
Best Indian Foods for How To Boost Metabolism Management
Traditional Indian Foods That Support Thermogenesis
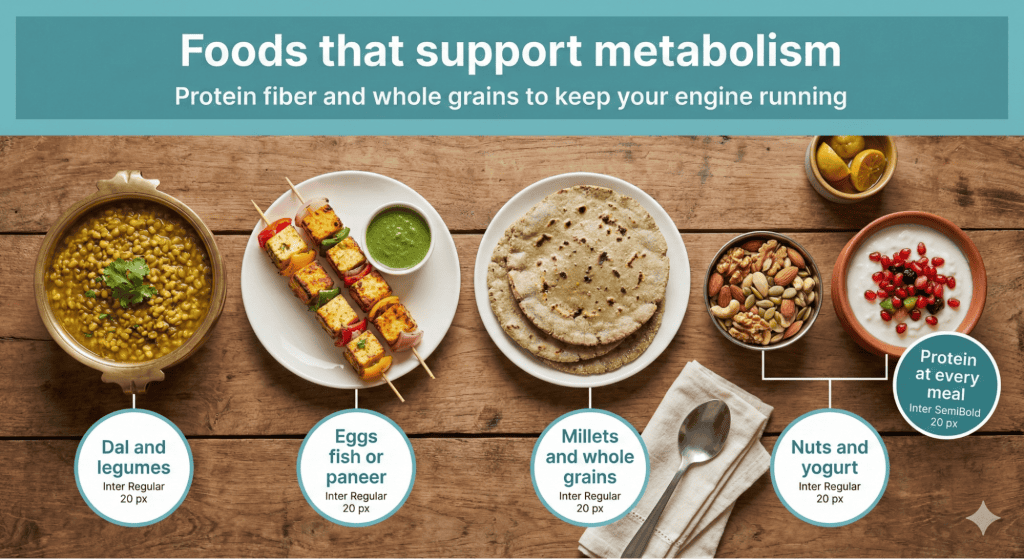
Indian cuisine offers excellent metabolism boosting foods when chosen strategically. Whole dals provide plant protein with high TEF, meaning 25 to 30% of their calories are burned during digestion. Include at least one dal daily. Additionally, eggs offer complete protein with one of the highest TEF of any food. Paneer provides protein though less than dal or eggs. For non-vegetarians, chicken and fish offer lean protein supporting muscle maintenance and high TEF.
Moreover, whole grains like brown rice, bajra, and jowar require more energy to digest than refined versions while providing sustained energy. Curd and buttermilk support gut health, which influences metabolic efficiency.
In fact, spices like black pepper, ginger, and turmeric provide negligible direct metabolic boost but make healthy foods taste good, supporting adherence. Include vegetables at every meal for fiber and nutrients supporting overall metabolic function rather than expecting them to burn significant calories directly.
Modern Indian Meal Options and Healthy Recipes
Create meals optimizing metabolic rate using Indian foods. For breakfast, try moong dal cheela loaded with vegetables plus paneer or eggs for protein. Make vegetable poha with peanuts and boiled egg. Additionally, prepare oats upma with nuts and milk for complete nutrition.
These high-protein breakfasts boost metabolism through TEF and prevent muscle loss. For lunch, ensure adequate protein through dal, paneer, chicken, or fish alongside whole grains and vegetables. Make mixed dal with extra protein added. Dinner could be lighter on carbs but still protein-focused with dal, eggs, or grilled chicken/paneer alongside vegetables.
Moreover, include protein-rich snacks like roasted chana, nuts, curd, or boiled eggs between meals to maintain stable blood sugar and muscle protein synthesis. These meal patterns support muscle maintenance and leverage TEF effectively, directly addressing how to boost metabolism through strategic food choices and timing.
Foods to Limit or Avoid for Better Results
Certain foods actively slow metabolism or prevent thermogenesis optimization. Refined carbs like white bread, maida products, and white rice cause insulin spikes without nutrients needed for metabolic function. Minimize these. Additionally, sugary drinks and sweets provide calories without satiety or nutrition, promoting fat storage. Excessive alcohol suppresses fat burning for 24+ hours after consumption and provides empty calories.
Moreover, ultra-processed packaged snacks contain trans fats and additives that may impair metabolic function. Foods high in added sugars cause insulin resistance over time, progressively slowing metabolism.
Furthermore, very low-calorie diets or extended fasting periods trigger metabolic adaptation, slowing metabolic rate to conserve energy. Therefore, adequate nutrition consistently supports metabolism better than extreme restriction or feast-famine patterns. Focus on whole foods in appropriate amounts rather than processed options or restrictive approaches that backfire metabolically.
Portion Sizes and Meal Timing for Indians
Portion control and timing influence metabolic rate through multiple pathways. Eating adequate total calories prevents metabolic slowdown from excessive restriction. Don’t drop below 1200 for women or 1500 for men. Additionally, distribute protein across meals rather than loading it all at dinner. Aim for 20 to 30 grams at breakfast, lunch, and dinner to optimize muscle protein synthesis.
Moreover, eat consistently at similar times daily to regulate metabolic hormones. Erratic timing confuses these systems. However, meal frequency matters less than total intake and protein distribution. Whether you eat 3 or 6 meals daily, ensure adequate protein and calories.
Furthermore, don’t fear eating at night if it fits your schedule and daily totals. The “no eating after 7 PM” rule has minimal metabolic impact. Use your hand for portions: palm for protein, fist for carbs, two fists for vegetables, thumb for fats. These guidelines prevent both under and overeating, supporting optimal metabolic rate.
Lifestyle Changes to Support How To Boost Metabolism
Metabolism Boosting Foods: The Right Approach for Indians
While no food magically melts fat, strategic choices boost metabolism through multiple mechanisms. Prioritize protein at every meal since it has 20 to 30% TEF compared to 5 to 10% for carbs and 0 to 3% for fat. This means 25 to 30% of protein calories are burned during digestion. Additionally, choose whole grains over refined for higher fiber content requiring more energy to digest and stabilizes blood sugar. Include metabolism boosting foods like green tea, coffee, and spices in moderation. They provide minimal caloric burn (10 to 20 calories daily) but enhance adherence if you enjoy them.
Moreover, stay hydrated with water as even mild dehydration can slow metabolic processes. Cold water provides negligible extra burn from warming it, but adequate hydration optimizes all metabolic functions. In fact, the real power of thermogenesis from food comes from eating adequate amounts consistently, especially protein, rather than restricting excessively, which triggers metabolic slowdown. Focus on what to add for metabolic benefit rather than what to eliminate.
Sleep and Stress Management Strategies
Sleep and stress management directly affect metabolic rate through hormonal pathways. Inadequate sleep reduces leptin and increases ghrelin, making you hungrier while slowing metabolism. Additionally, sleep deprivation impairs glucose metabolism and increases insulin resistance. Aim for 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep in a completely dark, cool room.
Moreover, chronic stress elevates cortisol constantly, promoting muscle breakdown and belly fat storage while suppressing metabolic rate. Practice daily stress management through whatever works for you: meditation, yoga, walking, deep breathing, or hobbies. Even 10 minutes daily significantly reduces cortisol.
Furthermore, poor sleep and high stress sabotage exercise recovery and motivation, indirectly reducing calorie burn from reduced activity and muscle building. Therefore, prioritizing these factors isn’t optional for metabolism repair but essential. Many people see dramatic improvements in energy and body composition simply from fixing sleep and stress before changing anything about food or exercise.
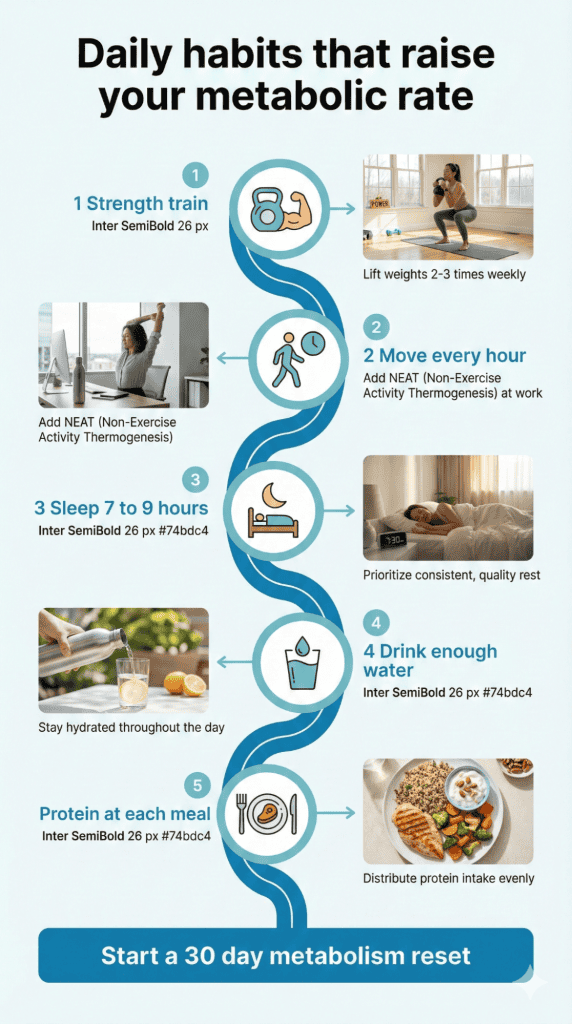
Daily Habits That Make a Real Difference
Small, consistent actions dramatically increase metabolism over time. Take stairs instead of elevators consistently, burning 5 to 10 extra calories per flight and maintaining muscle. Additionally, walk during phone calls, pace while thinking, do household chores actively. These NEAT activities add 200 to 400 calories daily. Stand or use a standing desk for part of your workday.
Moreover, include brief movement breaks every hour at work. Just 2 minutes of walking or stretching per hour significantly boosts daily burn. Drink water throughout the day as adequate hydration optimizes metabolic processes. Furthermore, expose yourself to slightly cooler temperatures occasionally, promoting brown fat activity that generates heat.
However, don’t expect dramatic results from cold showers or ice baths; the effect is minimal. In fact, the most powerful metabolism-boosting habit is strength training 2 to 3 times weekly, building muscle that permanently increases BMR. These habits compound over time, creating significant metabolic improvement without extreme measures.
Your 7-Day How To Boost Metabolism Management Meal Plan
This meal plan emphasizes protein, whole foods, and strategic timing for optimal metabolic rate:
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Evening Snack (4-5 PM) | Dinner (7-8 PM) |
| Day 1 | Moong dal cheela (2) + paneer (50g) + mint chutney + orange | Brown rice (1 katori) + dal (1 katori) + chicken (100g) + vegetables + salad | Roasted chana (1 bowl) + green tea | 2 rotis + palak dal + paneer tikka (50g) + raita |
| Day 2 | Vegetable poha + peanuts + 2 boiled eggs + milk | 2 rotis + chana dal + fish curry (100g) + mixed veg + curd | Apple with 8 almonds | Quinoa + dal tadka + grilled paneer (50g) + salad |
| Day 3 | Oats upma with vegetables + 6 walnuts + boiled egg + coffee | Brown rice + sambhar + chicken tikka (100g) + vegetables + raita | Sprout salad with lemon | 2 bajra rotis + dal + paneer bhurji + cucumber |
| Day 4 | 2 eggs scrambled + 2 whole wheat toast + banana + tea | 2 rotis + masoor dal + mixed veg + paneer (50g) + salad | Handful of roasted chana | Vegetable khichdi + 1 tbsp ghee + curd + egg |
| Day 5 | Moong dal dosa (2) + sambhar + paneer filling + coconut chutney | Brown rice + dal + fish (100g) + beans + raita | Fruit bowl with nuts | 2 rotis + rajma + vegetables + raita |
| Day 6 | Besan cheela (2) + vegetables + 2 boiled eggs + milk | 2 rotis + chana dal + chicken curry (100g) + salad + curd | Roasted makhana + green tea | Quinoa pulao + dal + paneer (50g) + vegetables |
| Day 7 | Idli (3) + sambhar + eggs (2) + coconut chutney + coffee | Brown rice + dal + mixed veg + paneer tikka (100g) + raita | 8 almonds + apple | 2 rotis + moong dal + grilled fish (100g) + salad |
Note: Each meal includes 20 to 30 grams of protein for optimal muscle preservation and TEF. Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water daily. Include strength training 2 to 3 times weekly for muscle building.
Common Mistakes Indians Make with How To Boost Metabolism
Diet Mistakes That Sabotage Progress
The biggest mistake is eating too few calories, thinking it speeds metabolism when it actually slows it through adaptive thermogenesis. Another error is not eating enough protein to preserve muscle during weight loss. Losing muscle dramatically reduces metabolic rate permanently. Additionally, people focus on “metabolism boosting foods” like green tea and spicy foods, expecting miracles when these provide negligible effects of 10 to 20 calories daily.
Moreover, excessive cardio without strength training burns calories acutely but doesn’t build metabolism-boosting muscle. Skipping meals erratically, thinking it “shocks” metabolism, is counterproductive. In fact, very low-carb diets can reduce thyroid function and metabolic rate when maintained long-term at very low calories.
Furthermore, people often chase the latest supplement or superfood instead of addressing basics: adequate protein, calories, and strength training. These mistakes keep metabolic rate suppressed despite efforts to improve it.
Lifestyle Pitfalls to Watch Out For
Many people sabotage their metabolism through lifestyle choices they don’t connect to the issue. Chronic sleep deprivation from overworking or screen time significantly slows metabolic rate through hormonal disruption. Additionally, constant dieting cycles create progressive metabolic slowdown with each attempt. Excessive sitting without breaks dramatically reduces NEAT and daily calorie burn.
Moreover, chronic stress keeps cortisol elevated, promoting muscle breakdown and metabolic suppression. Not strength training due to fear of looking “bulky” or cultural discomfort with weight rooms prevents building the muscle that permanently increases metabolism.
Furthermore, comparing your metabolism to friends’ ignores genetic differences that require individualized approaches. Taking metabolism-boosting supplements without addressing diet, exercise, and sleep fundamentals wastes money on minimal effects. In fact, many metabolism supplements contain dangerous levels of stimulants, causing more harm than good. Focus on proven lifestyle factors before chasing shortcuts.
How to Course-Correct When Things Go Wrong
If your efforts to boost metabolism aren’t working, evaluate systematically. Track your actual food intake for 3 days to verify you’re eating adequate protein and total calories. Maybe you’re unknowingly under-eating, triggering metabolic slowdown. Additionally, assess your strength training. Are you progressively overloading muscles or just going through motions without building strength? Muscle growth requires challenge.
Moreover, check your sleep quantity and quality. If getting less than 7 hours nightly, prioritize this before adding other interventions. Furthermore, evaluate stress levels honestly. High chronic stress prevents metabolic improvement regardless of diet and exercise perfection. If you’ve addressed all basics for 3 months without improvements in energy, body composition, or weight loss capability, see a doctor for thyroid and hormone testing.
Sometimes, underlying medical conditions need treatment. Work with a registered dietitian who understands metabolism repair if you’ve done prolonged extreme dieting requiring professional guidance for recovery.
Conclusion
How to boost metabolism isn’t about magic pills or superfoods but consistent application of science-backed strategies: building muscle through strength training, eating adequate protein to preserve muscle and leverage TEF, staying active throughout the day to maximize NEAT, sleeping adequately to optimize metabolic hormones, and managing stress to prevent cortisol-induced slowdown. Indians face genetic challenges with a lower baseline metabolic rate, but these same strategies work when applied consistently over months, not days.
Start today by adding one strength training session this week, even 20 minutes at home with bodyweight exercises. Ensure you’re eating at least 60 to 80 grams of protein daily, spread across meals. Additionally, commit to 7 to 8 hours of sleep nightly and take a 5-minute walking break every hour during work.
FAQs
Q1: What is how to boost metabolism and how does it affect Indians?
How to boost metabolism means increasing your metabolic rate, the calories your body burns at rest and during activity, through muscle building, adequate protein, and strategic movement. Indians face lower baseline metabolic rate than other populations due to genetic factors, higher body fat percentages, and lower muscle mass, requiring targeted strategies.
Q2: What are the main signs of a slow metabolic rate?
Signs include constant fatigue despite adequate sleep, feeling cold, especially in extremities, difficulty losing weight on low calories, slow recovery from exercise, brain fog, thinning hair, and brittle nails. Watch for weight gain despite normal eating, low energy throughout the day, and digestive issues like constipation, indicating a sluggish metabolic rate.
Q3: What foods should Indians eat for better metabolism boosting?
Eat adequate protein from dals, eggs, paneer, chicken, and fish at every meal to preserve muscle and leverage high TEF. Include whole grains like brown rice and millets, vegetables for fiber, and adequate total calories to prevent metabolic slowdown from restriction, supporting healthy thermogenesis.
Q4: Can metabolism be managed naturally?
Yes, increase metabolism naturally through strength training 2 to 3 times weekly to build muscle, eating adequate protein (1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram), 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep, stress management, and increasing daily movement. Avoid extreme low-calorie diets that trigger metabolic adaptation.
Q5: How long does it take to see results with metabolism improvements?
Energy improvements appear within 2 to 4 weeks of adequate protein, calories, and strength training. Measurable muscle gain and metabolic rate increases show within 8 to 12 weeks of consistent training and nutrition, with continued improvements over 6 to 12 months of dedicated effort, building metabolism-boosting muscle.