Hypothyroidism, also known as an underactive thyroid, is a common medical condition that occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce enough hormones. This can lead to a range of symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and depression. If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to more serious health problems. While there is no hypothyroidism cure, with proper hypothyroidism diagnosis and hypothyroidism treatment, individuals with hypothyroidism can lead healthy and productive lives. In this article, we will discuss hypothyroidism treatment, including the various hypothyroidism treatment options available, hypothyroidism diagnosis, hypothyroidism cure as well as lifestyle changes that can help with Thyroid Management.
Diagnosis of Hypothyroidism
Diagnosis is an essential step before someone undertakes hypothyroidism treatment. Hypothyroidism diagnosis can be done through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
Following are the steps in the hypothyroidism diagnosis:-
- Evaluation of the patient’s symptoms: The first step in the hypothyroidism diagnosis is a thorough evaluation of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and family history. The healthcare provider may perform a physical examination to check for signs of hypothyroidism such as a slow heart rate, dry skin, and brittle nails.
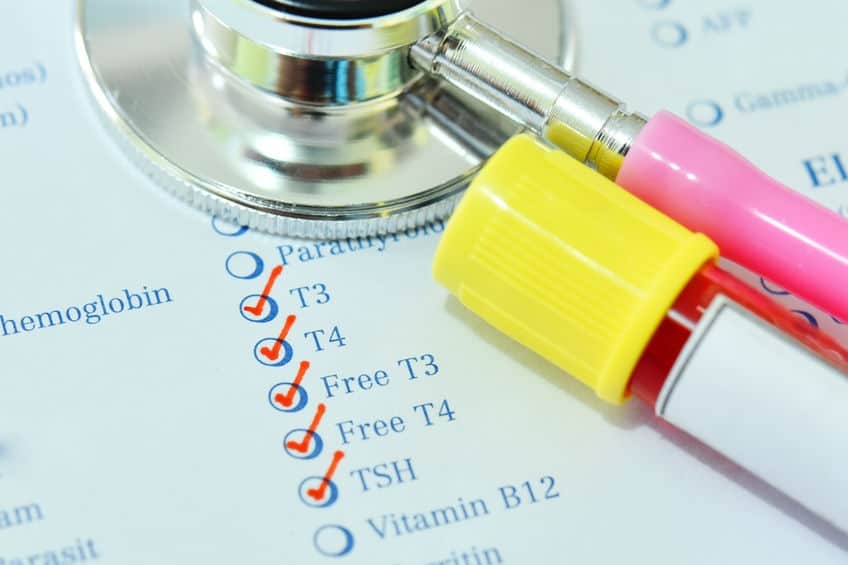
- Perform blood tests: The next step is to perform blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4). In some cases, additional tests such as triiodothyronine (T3) or thyroid peroxidase antibodies may be ordered to confirm the hypothyroidism diagnosis or identify the underlying cause of hypothyroidism.
Nonetheless, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before undertaking any hypothyroidism treatment. Choosing someone who is knowledgeable and experienced in hypothyroidism diagnosis and management, is equally critical. Get a better understanding of Hypothyroid Meaning & Causes.
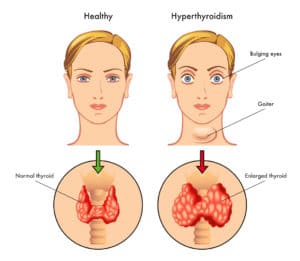
Some common symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
- Fatigue and weakness: Individuals with hypothyroidism often feel tired, sluggish, and lacking in energy, even after getting enough sleep.
- Weight gain: Hypothyroidism can cause a slow metabolism, leading to weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
- Cold intolerance: People with hypothyroidism may feel cold even in warm temperatures.
- Dry skin and hair: Hypothyroidism can cause dry, itchy skin and brittle hair that may fall out easily.
- Constipation: Low levels of thyroid hormone can slow down the digestive system, leading to constipation.
- Muscle aches and joint pain: Hypothyroidism can cause muscle weakness and stiffness, as well as joint pain and swelling.
- Depression: Low levels of thyroid hormone can affect mood and cause feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and irritability.
- Irregular menstrual periods: Women with hypothyroidism may experience heavy or irregular menstrual periods, or even miss periods altogether.
- Cognitive impairment: In some cases, hypothyroidism can cause brain fog, poor concentration, and memory problems.
Treatment of Hypothyroidism
The goal of hypothyroidism treatment is to replace the missing thyroid hormones and restore normal thyroid function. The most common hypothyroidism treatment options for hypothyroidism cure include:
- Hormone replacement therapy: This involves taking daily doses of synthetic thyroid hormone (levothyroxine) in the form of a pill. The dose is adjusted based on the patient’s age, weight, and severity of hypothyroidism, and may need to be monitored and adjusted over time.
- Nutritional supplements: In some cases, deficiencies in certain nutrients such as iodine, selenium, and zinc may contribute to hypothyroidism. Supplementing these nutrients can help support thyroid function.
- Lifestyle modifications: Certain lifestyle changes such as a healthy Thyroid Diet Plan, regular exercise, stress management, and getting adequate sleep can help support thyroid function and improve overall health.
- Treating underlying conditions: If hypothyroidism is caused by an underlying condition such as an autoimmune disease or a pituitary disorder, treating that condition may help improve thyroid function go through our Thyroid Blogs for more information.
The most common causes of hypothyroidism include:
- Autoimmune disease: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage. This is the most common cause of hypothyroidism.
- Surgical removal of the thyroid gland: If the thyroid gland is surgically removed due to cancer or other conditions, hypothyroidism can occur.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy used to treat cancers of the head and neck can damage the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism.
- Medications: Certain medications such as lithium, amiodarone, and interferon alpha can interfere with thyroid function and cause hypothyroidism.
- Congenital hypothyroidism: Some babies are born with an underactive thyroid gland due to genetic factors or a lack of iodine during pregnancy.
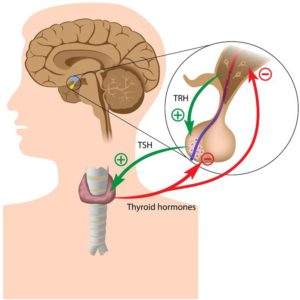
- Pituitary gland disorders: The pituitary gland in the brain produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which signals the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. If the pituitary gland is not functioning properly, it can lead to hypothyroidism.
- Aging: As we age, the thyroid gland may become less efficient in producing thyroid hormones, leading to hypothyroidism.
Home Remedies & Lifestyle Tips to Treat Hypothyroidism
While there is no hypothyroidism cure, there are some home remedies and lifestyle tips that may help manage symptoms and support overall thyroid function. These include:
- Eating a balanced diet: Consuming a diet with Thyroid Recipes rich in nutrients such as iodine, selenium, and zinc can help support thyroid function. Foods that are good sources of these nutrients include seafood, seaweed, eggs, nuts, and whole grains.
- Reducing stress: Stress can interfere with thyroid function, so practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and improve overall health.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve metabolism, support thyroid function, and reduce the risk of weight gain, which is a common symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Getting adequate sleep: Adequate sleep is important for overall health and can help reduce stress, improve mood, and support thyroid function.
- Avoiding certain foods: Some foods may interfere with thyroid function or the absorption of thyroid hormone medication, such as soy, cruciferous vegetables, and high-fiber foods.
- Supplementing with vitamins and minerals: Supplements such as vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics may help support thyroid function and improve overall health.
It is important to note that while these home remedies and lifestyle tips may help manage symptoms and support thyroid function, they should not replace proper hypothyroidism treatment. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate hypothyroidism treatment plan for hypothyroidism cure.
The Bottom Line
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland fails to produce enough thyroid hormones, resulting in a variety of symptoms such as weight gain, fatigue, and depression. The most common causes of hypothyroidism include autoimmune disease, surgical removal of the thyroid gland, radiation therapy, medications, and congenital hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism treatment typically involves hormone replacement therapy, nutritional supplements, lifestyle modifications, and treating underlying conditions. Moreover, while there is no Hypothyroidism cure, home remedies and lifestyle tips such as eating a balanced diet, reducing stress, regular exercise, and getting adequate sleep may help manage symptoms and support overall thyroid function. However, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate hypothyroidism treatment plan and hypothyroidism diagnosis.
FAQs
How can I cure Hypothyroidism Naturally?
It is important to note that while these remedies may help manage symptoms and support thyroid function, a hypothyroidism cure should not replace proper medical treatment.
- Eating a balanced diet: Consuming a diet rich in nutrients such as iodine, selenium, and zinc can help support thyroid function. Foods that are good sources of these nutrients include seafood, seaweed, eggs, nuts, and whole grains.
- Reducing stress: Stress can interfere with thyroid function, so practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and improve overall health.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve metabolism, support thyroid function, and reduce the risk of weight gain, which is a common symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Getting adequate sleep: Adequate sleep is important for overall health and can help reduce stress, improve mood, and support thyroid function.
- Avoiding certain foods: Some foods may interfere with thyroid function or the absorption of thyroid hormone medication, such as soy, cruciferous vegetables, and high-fiber foods.
- Supplementing with vitamins and minerals: Supplements such as vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics may help support thyroid function and improve overall health.
What is the Best Treatment for Hypothyroidism?
While there is no hypothyroidism cure, the best hypothyroidism treatment depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. Some of the common treatments have been mentioned below:-
- In general, the most common hypothyroidism treatment is hormone replacement therapy, which involves taking synthetic thyroid hormone medication daily to replace the deficient thyroid hormone.
- The most commonly prescribed medication for hypothyroidism is levothyroxine, which is a synthetic form of the hormone thyroxine. This medication is usually taken orally and is effective in replacing the missing thyroid hormone in the body.
- In addition to hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management may help manage symptoms and support overall thyroid function.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate hypothyroidism treatment, monitor thyroid function, and adjust hypothyroidism treatment and hypothyroidism diagnosis as needed.
Can Hypothyroidism be cured completely?
In most cases, there is no hypothyroidism cure, but it can be effectively managed with proper medical treatment. Overall, remission and better management of hypothyroidism is a possibility with proper medical treatment and a hypothyroidism diagnosis, allowing individuals to lead normal, healthy lives.
Can Hypothyroidism be cured by Exercise?
While regular exercise is an important component of a healthy lifestyle and may help manage symptoms of hypothyroidism, it cannot help with hypothyroidism cure. Hypothyroidism typically requires medical treatment such as hormone replacement therapy. However, regular exercise can help improve the symptom of hypothyroidism.
Having said that, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate hypothyroidism treatment plan and hypothyroidism diagnosis, which may include medication, lifestyle modifications, and other interventions as needed.
Which is the best hypothyroidism cure?
While there is no hypothyroidism treatment that can guarantee hypothyroidism cure, one can consume the following to better manage it:-
- Dairy products high in iodine
- Beans
- Iodine supplements
- Almonds
- Apple cider vinegar
- Coconut oil
- Ginger