Before knowing the symptoms of Hypothyroid, it is essential to know what causes hypothyroidism in the first place. Hypothyroidism or Hypothyroid, also known as an underactive thyroid, is a common endocrine disorder that occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. This butterfly-shaped gland, located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, body temperature, and energy levels. When thyroid hormone levels drop below normal, it can lead to a wide range of hypothyroidism symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain, hair loss, and depression. There are several causes of hypothyroid symptoms, including autoimmune disease, radiation therapy, and certain medications. While hypothyroid is a chronic condition that requires ongoing Thyroid Management, with proper treatment, most people with the condition can lead normal, healthy lives while keeping their hypothyroid symptoms at bay. Here, we shall understand what causes hypothyroidism, how to identify hypothyroid symptoms and how to control hypothyroidism causes.
What are the Symptoms of Hypothyroidism?
Before knowing what causes hypothyroidism, let’s understand the variety of its symptoms. Hypothyroidism symptoms can vary widely from person to person, and they may develop gradually over a period of months or years. Some of the most common hypothyroidism symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness: People with hypothyroid often feel tired and sluggish, even after getting enough sleep.
- Weight gain: Hypothyroid symptoms can also include slowing down metabolism, causing weight gain and difficulty in losing weight.
- Cold intolerance: People with hypothyroid symptoms may feel cold all the time, even in warm environments.
- Dry skin and hair: Hypothyroid symptoms can include dry skin, hair loss, and brittle nails.
- Depression and anxiety: Hypothyroid symptoms can affect mood and lead to depression and anxiety.
- Constipation: Hypothyroid symptoms can cause slow metabolism which can lead to constipation.
- Menstrual irregularities: Hypothyroidism can affect menstrual cycles and cause heavy or irregular periods.
- Muscle and joint pain: People with hypothyroid may experience muscle weakness and pain, as well as joint stiffness.
It is important to note that not everyone with hypothyroid will experience all of these hypothyroidism symptoms, and some people may not experience any hypothyroidism symptoms at all. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine if hypothyroidism may be the cause.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism in Males
Before knowing what causes hypothyroidism in males, let’s understand the variety of its symptoms. While the hypothyroidism symptoms can vary among individuals. There are some common symptoms of hypothyroidism in males. Here are some of the hypothyroidism symptoms that are more prevalent in males:
- Erectile dysfunction: One of the most common symptoms of hypothyroidism in males can include low testosterone levels and cause difficulty with erections.
- Decreased libido: Hypothyroid can affect sexual desire and lead to decreased libido.
- Muscle weakness: Hypothyroid can cause muscle weakness and aches, particularly in the arms, legs, and hips.
- Fatigue: Males with hypothyroid may experience fatigue, particularly in the afternoon.
- Weight gain: Another one of the most common symptoms of hypothyroidism in males is weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
- Hair loss and dry skin: One of the commonly heard symptoms of hypothyroidism in males is hair loss and dry, itchy skin.
- Depression and anxiety: Hypothyroidism can affect mood and lead to depression and anxiety.
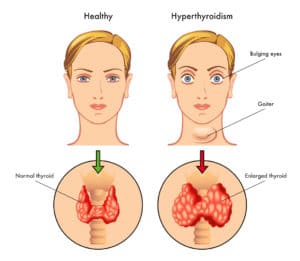
- Enlarged thyroid gland: Some males with hypothyroidism may develop an enlarged thyroid gland, also known as a goiter.
Hence, if these symptoms of hypothyroidism in males are a common sight, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for these hypothyroidism symptoms. It’s important to note that these hypothyroidism symptoms can be caused by other health conditions as well, so it’s essential to have proper diagnosis, thyroid test at home, and treatment plan.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism in Females
Hypothyroidism symptoms can vary among individuals and can be different between males and females. However, there are some common symptoms of hypothyroidism in females, particularly those of reproductive age. Here are some of the hypothyroidism symptoms that are more prevalent in females:
- Menstrual irregularities: One of the most common symptoms of hypothyroidism in females is heavier, more frequent, or more painful periods.
- Infertility: Hypothyroidism can make it more difficult to conceive.
- Pregnancy complications: Untreated hypothyroidism during pregnancy can increase the risk of miscarriage, premature birth, and preeclampsia.
- Depression and anxiety: Hypothyroidism can affect mood and cause depression and anxiety, which are more common in females.
- Weight gain: Another one of the most common symptoms of hypothyroidism in females is weight gain or difficulty losing weight, particularly in the hips and thighs.
- Hair loss and dry skin: One of the commonly heard symptoms of hypothyroidism in females includes hair loss and dry, itchy skin.
- Fatigue and weakness: Females with hypothyroidism may experience fatigue and weakness, particularly in the morning.
- Brain fog: Hypothyroid can affect cognitive function, leading to difficulties with memory, concentration, and attention.
Hence, if these symptoms of hypothyroidism in females are a common sight, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for these hypothyroidism symptoms.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism in Teens & Children
Hypothyroidism can affect individuals of any age, including children and teenagers. The symptoms of hypothyroidism in teens and children may vary depending on the age of the child and the severity of the condition. Here are some common symptoms of hypothyroidism in teens and children:
- Slow growth: Children with hypothyroidism may have slower growth and delayed puberty.
- Poor weight gain: Infants and young children with hypothyroidism may have poor weight gain and may be shorter than average.
- Delayed development: Children with hypothyroidism may have delayed development, including delayed speech, walking, and other milestones.
- Constipation: Hypothyroidism can cause constipation, which can be particularly problematic in infants and young children who are still developing their bowel habits.
- Poor school performance: Children with hypothyroidism may have difficulty with memory and concentration, leading to poor school performance.
- Dry skin and hair: Hypothyroidism can cause dry skin, brittle nails, and hair loss in children and teens.
- Fatigue and weakness: Teens and children with hypothyroidism may experience fatigue and weakness, which can affect their ability to participate in daily activities.
- Mood changes: Hypothyroidism can affect mood and cause irritability, anxiety, and depression in teens and children.
If you suspect that your child or teenager may have hypothyroidism, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism in Infants
Hypothyroidism is a condition that can affect infants, and if left untreated, it can lead to serious developmental and intellectual disabilities. The symptoms of hypothyroidism in children may vary from person to person. However, here are some common symptoms of hypothyroidism in infants:
- Poor feeding: One of the hypothyroidism symptoms in infants includes having difficulty feeding, being less interested in nursing or bottle-feeding, or having a weak suck.
- Sleepiness: One of the most common hypothyroidism symptoms in infants may be being excessively sleepy and facing difficulty to arouse.
- Constipation: Another one of the symptoms of hypothyroidism in infants includes constipation in infants, leading to hard stools and difficulty passing stool.
- Jaundice: Symptoms of hypothyroidism in children may include developing jaundice, and a yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Puffy face and swollen tongue: Symptoms of hypothyroidism in infants also include a puffy face and a swollen tongue in infants.
- Slow growth: Infants with hypothyroidism may have slow growth and may not reach developmental milestones on time.
- Large fontanelles: Symptoms of hypothyroidism in children can cause the soft spots on an infant’s head to stay open for longer than usual.
- Hoarse cry: Symptoms of hypothyroidism in infants may include having a hoarse cry or voice as well.
If you suspect any of these symptoms of hypothyroidism in infants, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan with comprehensive Thyroid Recipes.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces insufficient amounts of thyroid hormones. The hypothyroidism causes can vary, but here are some common ones to understand what causes hypothyroidism:
- Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis): This is one of the most common hypothyroidism causes. It occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage to the gland.
- Radioactive iodine treatment or surgery: Treatment for hyperthyroidism, which involves the use of radioactive iodine or surgery to remove the thyroid gland, can sometimes result in hypothyroidism. Hence, it can also be considered one of the hypothyroidism causes.
- Medications: Hypothyroidism causes may also include medications. Certain medications, such as lithium, interferon alpha, and amiodarone, can cause hypothyroidism.
- Congenital hypothyroidism: This is a rare form of hypothyroidism that is present at birth. It can be caused by genetic defects or developmental abnormalities in the thyroid gland. Hence, genetic defects can also be one of the hypothyroidism causes.
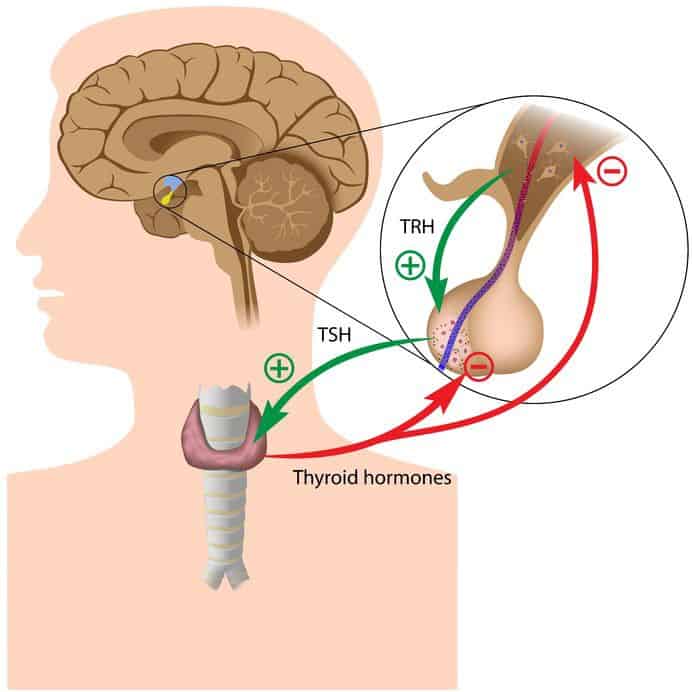
- Pituitary gland disorders: The pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which signals the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. Disorders that affect the pituitary gland can lead to hypothyroidism. This can be one of the hypothyroidism causes.
- Iodine deficiency: One of the hypothyroidism causes can also be Iodine deficiency. Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. A deficiency of iodine can lead to hypothyroidism.
- Pregnancy: Hypothyroidism can develop during pregnancy, particularly in women with a history of thyroid problems or autoimmune disorders.
Now that you know what causes hypothyroidism, it’s important to note that these are not the only hypothyroidism causes, and sometimes the cause is unknown. If you suspect that you may have any of these hypothyroidism symptoms, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis of the hypothyroidism causes and a treatment plan.
When to See a Doctor for Hypothyroidism
If you are experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Here are some situations in which you should consider seeing a doctor for hypothyroidism:
- You are experiencing symptoms: Symptoms of hypothyroidism can be vague and may be attributed to other conditions. If you are experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, or cold intolerance, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine if hypothyroidism may be the cause.
- You have a family history of thyroid problems: If you have a family history of thyroid problems, you may be at higher risk for developing hypothyroidism. It’s important to discuss your family history with a healthcare provider and have your thyroid function checked regularly.
- You are pregnant: Hypothyroidism can develop during pregnancy, and it’s important to have your thyroid function checked regularly if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
- You have a history of autoimmune disorders: Autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, can increase the risk of developing hypothyroidism. If you have a history of autoimmune disorders, it’s important to have your thyroid function checked regularly.
- You are taking medications that can affect the thyroid gland: Certain medications, such as lithium, interferon alpha, and amiodarone, can affect the thyroid gland and increase the risk of hypothyroidism.
If you are experiencing any of these situations or are concerned about hypothyroidism, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider or go through our Thyroid Blogs for further evaluation and treatment.
What are the Risk Factors Associated with Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a common condition, and there are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing it. Some of the common risk factors associated with hypothyroidism include:
- Age: Hypothyroidism is more common in people over the age of 60.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop hypothyroidism than men.
- Family history: If a family member has hypothyroidism or other thyroid problems, you may be at increased risk.
- Autoimmune disorders: If you have an autoimmune disorder, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, you may be at increased risk for hypothyroidism.
- Previous thyroid surgery or radiation treatment: If you have had surgery or radiation treatment to the thyroid gland, you may be at increased risk for hypothyroidism.
- Iodine deficiency: Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones, and a deficiency in iodine can increase the risk of hypothyroidism.
- Pregnancy: Hypothyroidism can develop during pregnancy, particularly in women with a history of thyroid problems or autoimmune disorders.
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can increase the risk of hypothyroidism.
It’s important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not mean that you will definitely develop hypothyroidism. It is imperative that you know what causes hypothyroidism before you conclude that you have hypothyroidism. However, if you are at increased risk, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider about monitoring your thyroid function and managing any symptoms that may arise.
The Bottom Line
This blog makes you understand what causes hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Common symptoms of hypothyroidism in male and females include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and dry skin. The symptoms of hypothyroidism in children may include slowed growth, delayed development, constipation and the like. The condition can affect individuals of any age or gender, but women, older individuals, and those with a family history of thyroid problems or autoimmune disorders are at a higher risk. Other risk factors include iodine deficiency, previous thyroid surgery or radiation treatment, certain medications, and pregnancy. If you suspect any of these hypothyroid symptoms, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
FAQs
Can Hypothyroid symptoms appear suddenly?
To know what causes hypothyroidism, it is essential to recognize different symptoms. While hypothyroidism typically develops slowly over time, in some cases, hypothyroidism symptoms can appear suddenly. This is particularly true for people who have had their thyroid gland removed or who have undergone radioactive iodine therapy for thyroid cancer or other thyroid conditions. In some cases, a sudden onset of hypothyroid symptoms may also occur as a result of a pituitary gland problem or an autoimmune disorder, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or postpartum thyroiditis. It’s important to note that the sudden onset of symptoms may also be caused by other medical conditions, so it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What are the early signs and symptoms of Hypothroid?
While you’ve understood what causes hypothyroidism, here are some early signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism:
- Feeling tired or sluggish, even after getting enough sleep, is a common early symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight can be an early sign of hypothyroidism.
- Feeling cold or having a lower tolerance for cold temperatures than usual can be an early symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Dry skin, hair, and nails can be an early sign of hypothyroidism.
- Constipation or difficulty passing stools can be an early symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Changes in mood, including depression or anxiety, can be an early sign of hypothyroidism.
- Weakness or pain in the muscles, particularly in the arms and legs, can be an early symptom of hypothyroidism.
If you have any of these hypothyroidism symptoms, it is critical to consult a healthcare provider. So, stop waiting and become our next Thyroid Success Story!
What are the common symptoms of Hypothyroid?
To understand what causes hypothyroidism, it is important to know some of the most common hypothyroidism symptoms including:
- Feeling tired or sluggish, even after getting enough sleep, is a common symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight can be a symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Feeling cold or having a lower tolerance for cold temperatures than usual can be a symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Dry skin, hair, and nails can be a symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Constipation or difficulty passing stools can be a symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Changes in mood, including depression or anxiety, can be a symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Joint pain and stiffness: Hypothyroidism can cause joint pain and stiffness, particularly in the hands and feet.
- Women with hypothyroidism may experience irregular or heavy menstrual periods.
What are the warning signs of Hypothyroid?
To know what causes hypothyroidism, it is essential to understand its warning signs. While some people with hypothyroidism may not experience any hypothyroidism symptoms, there are some warning signs to be aware of, including:
- Feeling extremely tired or exhausted, even after getting enough rest.
- Feeling cold or having a lower tolerance for cold temperatures than usual.
- Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
- Thinning hair or hair loss, particularly from the scalp, eyebrows, and other areas of the body.
- Changes in mood, including depression or anxiety.
- Weakness or pain in the muscles, particularly in the arms and legs.
- Irregular or heavy periods: Women with hypothyroidism may experience irregular or heavy menstrual periods.
- High cholesterol: Hypothyroidism can cause high cholesterol levels.
It’s important to read about the science of thyroid and note that these hypothyroidism symptoms can be caused by other medical conditions as well.