Beans are a staple in many cuisines around the world and are valued for their versatility, flavor, and nutritional benefits. In addition to being a rich source of protein and fiber, beans also provide a range of vitamins and minerals that are essential for overall health and well-being. Whether you’re looking to build muscle, manage your weight, or simply increase your nutrient intake, beans can be a nutritious and delicious addition to your diet. In this article, we’ll explore the nutritional value of beans, including their calorie, protein, and carbohydrate content, and examine some of the potential health benefits of incorporating beans into your meals.
Nutritional Value of Beans
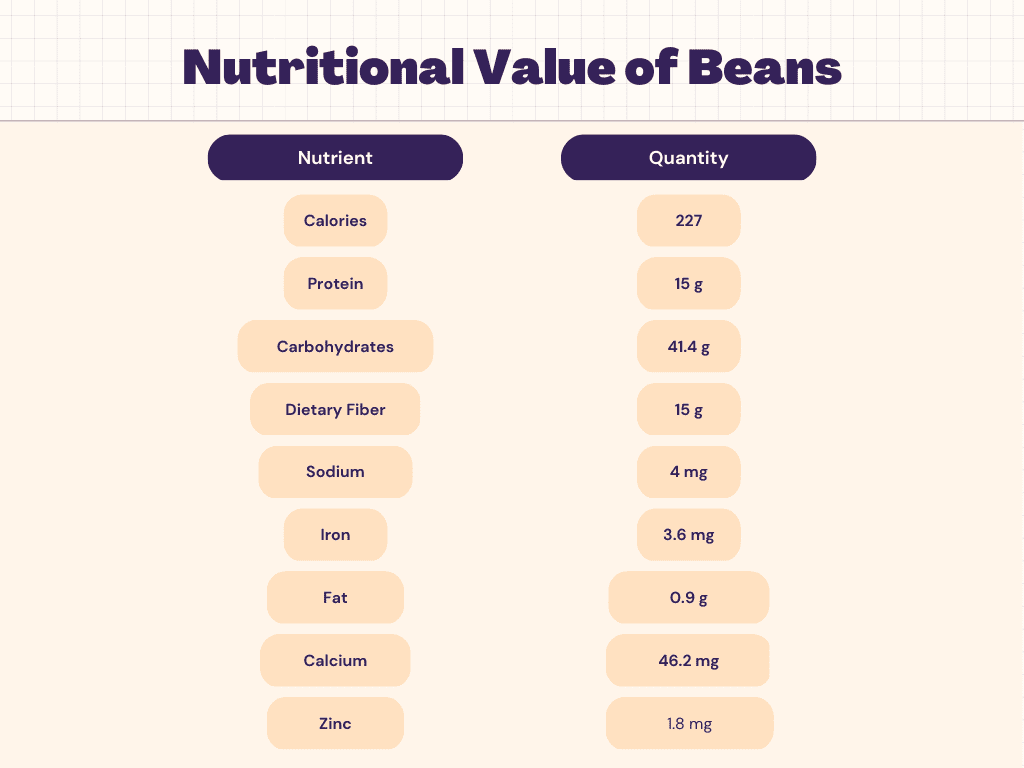
Nutritional Facts of Beans
Carbs In Beans
Beans are a good source of carbohydrates, which are the body’s primary source of energy. Most beans are considered complex carbohydrates, which means they are made up of long chains of sugar molecules that the body breaks down slowly, providing a steady stream of energy over time. One cup of cooked beans typically contains around 40-45 grams of carbohydrates, with most of these coming from dietary fiber. Fiber is an important type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest or absorb, but that provides numerous health benefits, including regulating blood sugar, promoting feelings of fullness, and supporting digestive health. In addition, beans are a low glycemic index food, which means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels and can help to prevent spikes and crashes in energy.
Protein In Beans
Beans are an excellent source of plant-based protein, which is important for maintaining and repairing tissues in the body, building muscle mass, and supporting a healthy immune system. Depending on the type of beans, one cup of cooked beans can contain anywhere from 14-18 grams of protein. This makes beans a valuable protein source for vegetarians, vegans, and others who may not consume meat or dairy products. In addition, beans are also rich in other essential nutrients, such as iron, magnesium, and zinc, which work together with protein to support a range of bodily functions. The protein in beans is also easier on the digestive system than animal protein, which can be harder to digest and may contribute to inflammation or other health issues over time.
Health Benefits Of Beans
Beans offer a wide range of health benefits that make them a valuable addition to any diet, particularly for those managing conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, PCOS, or seeking to achieve healthy weight loss.
- Beans have a low glycemic index, which means they don’t cause significant spikes in blood sugar levels, making them an ideal food choice for people with diabetes. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
- They are also rich in dietary fiber, which helps to slow the absorption of carbohydrates in the body, further supporting healthy blood sugar management. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
- In addition, the high fiber content in beans can also help regulate digestion, promote feelings of fullness, and support healthy weight loss efforts. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
- The magnesium and zinc in beans play important roles in thyroid function, while the protein content can support healthy muscle mass and immune function in people with PCOS. Check our PCOS Plans here.
Overall, beans are a nutritious, versatile food that can offer numerous health benefits when incorporated into a balanced diet.
Vitamins & Minerals in Beans
Beans are a nutrient-dense food that provides a range of essential vitamins and minerals. These include B vitamins, which are important for energy metabolism, iron, which supports the production of red blood cells and oxygen transport, magnesium, which plays a role in numerous bodily functions, including bone health and nerve function, and potassium, which is important for regulating blood pressure and supporting healthy muscle function. In addition, beans are also rich in zinc, which supports immune function, and copper, which plays a role in the formation of collagen and supports healthy skin, hair, and nails. Some types of beans are also a good source of calcium, which is important for bone health, and folate, which is essential for healthy fetal development during pregnancy. Overall, the nutrient profile of beans makes them a valuable addition to any diet.
The Bottom Line
Beans are a highly nutritious food that offers a range of health benefits. They are an excellent source of plant-based protein, which is important for building and repairing tissues, and they are also rich in a variety of essential vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins, iron, magnesium, potassium, zinc, and copper. In addition, beans are a low glycemic index food and a good source of dietary fiber, which can support healthy blood sugar management, digestion, and weight loss. The nutrient profile of beans makes them an ideal food choice for people managing diabetes, thyroid disorders, PCOS, or seeking healthy weight loss.
Faqs
How many Beans can I eat in a day?
The amount of beans you can eat in a day depends on your individual dietary needs and preferences. As a general guideline, a serving size of cooked beans is about 1/2 cup or 85 grams. The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes aim to consume at least three to five servings of beans per week. However, if you are not used to eating beans, it is best to start with a small portion and gradually increase your intake to avoid digestive discomfort. If you have specific dietary concerns or medical conditions, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine the right amount of beans for your needs.
Should I eat Beans before or after exercise?
Beans are a nutrient-dense food that can provide a source of energy to support physical activity. However, the timing of bean consumption in relation to exercise depends on your individual needs and preferences. Eating beans before exercise can provide a source of slow-releasing carbohydrates that can help fuel your workout and sustain energy levels. On the other hand, eating beans after exercise can help support recovery by providing protein and nutrients that can aid in muscle repair and growth. Additionally, beans can help replenish glycogen stores and support healthy blood sugar levels after exercise. Ultimately, it’s best to experiment with different timing strategies to determine what works best for you and your body.
What are the benefits of Beans?
Beans offer a range of health benefits due to their nutrient-dense profile. Some of the potential benefits of eating beans include:
- Improved blood sugar control: Beans are a low glycemic index food that can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Digestive health: Beans are a good source of dietary fiber, which can support healthy digestion, improve bowel regularity, and reduce the risk of colon cancer.
- Heart health: The high fiber and potassium content in beans can help lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve overall heart health.
- Weight management: Beans are a low-fat, high-fiber food that can help promote feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake, making them a great food choice for weight management.
- Nutrient-dense: Beans are rich in a variety of essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, magnesium, and zinc, which are important for maintaining overall health and wellness.
- Cost-effective: Beans are an inexpensive and versatile source of plant-based protein that can be used in a variety of recipes, making them a cost-effective and healthy addition to any diet.
What is the best time to eat Beans?
There is no one “best” time to eat beans, as it largely depends on your individual needs and preferences. However, there are a few different ways to incorporate beans into your diet to maximize their health benefits:
- As a part of a balanced meal: Adding beans to a balanced meal that includes a variety of other nutrients can help you feel full and satisfied while providing a range of essential vitamins and minerals.
- As a pre-workout snack: Eating beans before a workout can provide a source of slow-releasing carbohydrates that can help fuel your workout and sustain energy levels.
- As a post-workout meal: Eating beans after exercise can help support recovery by providing protein and nutrients that can aid in muscle repair and growth.
- As a healthy snack: Beans can be eaten as a healthy snack on their own, or combined with other ingredients to create a tasty and nutrient-dense snack.
Ultimately, the timing of bean consumption should be based on your individual needs and preferences, as well as the context of your overall diet and lifestyle.