Indian cuisine is where ghee, a form of clarified or drawn butter, first appeared. The method of cooking used to separate milk solids and water from fat is known as clarification. Unlike clarified butter, which is heated for a shorter period of time, ghee allows milk solids to color before being squeezed off. Compared to conventional clarified butter, ghee has a deeper, nuttier flavor as a result.
Nutritional Value of Ghee
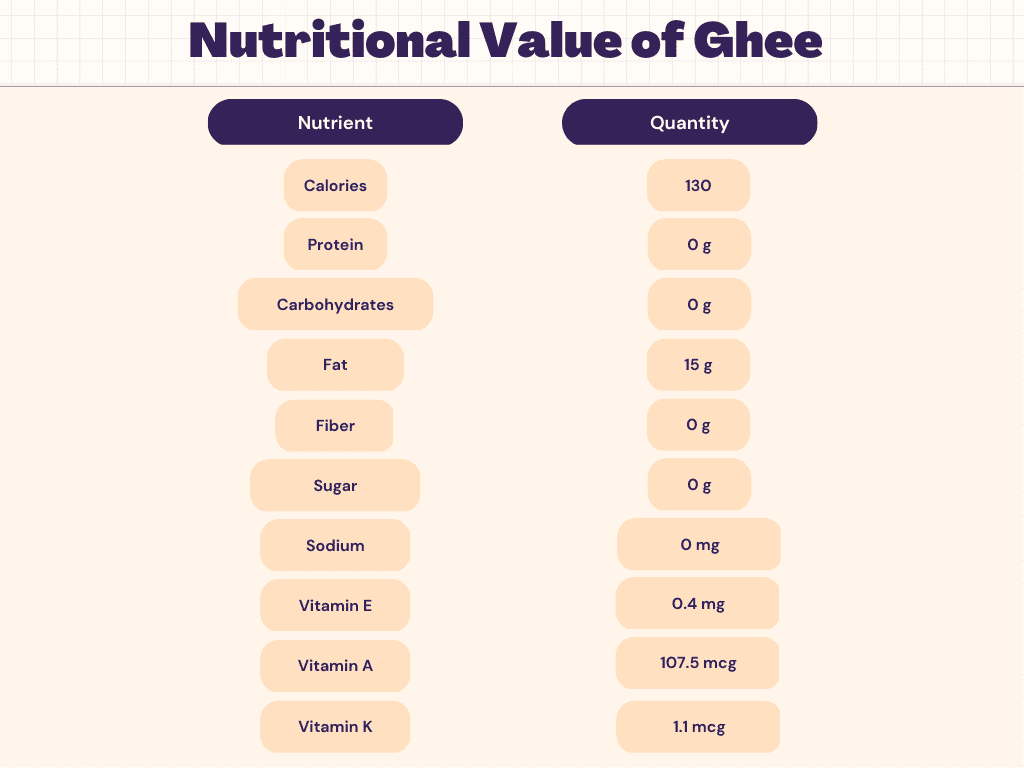
Nutritional Facts of Ghee
Carbs
Ghee has no carbs because it is virtually entirely composed of fat.
Fat
Ghee is almost entirely fat, like the majority of cooking oils. 15 grams of fat—9 grams of which are saturated fat—are present in one tablespoon. Less than one gram of polyunsaturated fat and around 5 grams of healthy monounsaturated fat make up the remaining fat content.
Protein
If the milk solids (whey) aren’t completely removed after the clarifying process, ghee may still include traces of protein.
Health Benefits Of Ghee
- Helps in healing of skin – has skin-healing qualities due to antibacterial and antioxidant activity, perhaps as a result of the presence of vitamins A and E. However, several research examined ghee when combined with honey, which also has advantageous effects.
- Reduces gut inflammation – Butyric acid, a short-chain fatty acid found in ghee, has been associated with reduced inflammation and better digestive health.
- Supports heart health – Omega-3 fatty acids found in ghee may reduce inflammation and provide heart disease protection.
Vitamins & Minerals in Ghee
Ghee’s micronutrient content can vary depending on the brand and the diet of the cows that provided the milk for it. A teaspoon typically provides 8% of the RDI for vitamin A, 2% of the RDI for vitamin E, and 1% of the RDI for vitamin K.
The Bottom Line
One variety of clarified butter is ghee. Due to the removal of the water and milk solids, it has a higher concentration of fat than butter. It has been utilized for countless years in Indian and Pakistani cultures. The word is derived from a Sanskrit word that means “sprinkled.” In order to keep the butter from going bad in warm weather, ghee was developed.
FAQs
How much Ghee can I eat in a day?
Ghee should be a part of at least one of your daily meals because it is full of vitamins that are vital for the immune system. Make sure you consume 3-6 tsp of ghee every day/per person.
Should I eat Ghee before or after exercise?
You should eat something with proteins before beginning your workout if you want to do something much more intensive, like strength training or HIIT (High Intensity Interval Training).
What is the best time to eat Ghee?
Ghee is a vital source of fuel for every single cell in the body, and taking it first thing in the morning on an empty stomach treats the body like rasa. Ghee is unquestionably regarded as a healthy fat and is frequently advised to be ingested uncooked by dripping it over hot cooked dishes.
What are the benefits of Ghee?
- Has Good Fats. Ghee has been shown by research to be low in fat.
- aids the digestive system A healthy gut is closely tied to ghee consumption.
- builds up the immune system.
- Provider of Vital Vitamins.
- cancer-preventative
- anti-inflammatory
- Lactose intolerance benefits.
- Cares for Burns.
- wholesome skin.