Millet is a versatile and nutritious grain that has been a staple food in many cultures for thousands of years. It is a rich source of calories, protein, and carbohydrates, making it an important food for people looking to maintain a healthy diet. Millet is gluten-free, which makes it a good option for people with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. In addition, it is low in fat and high in fiber, making it a filling and healthy food choice. Whether you are looking to increase your calorie intake, improve your protein intake, or simply want a nutritious and delicious food option, millet is a great choice.
Nutritional Value of Millet
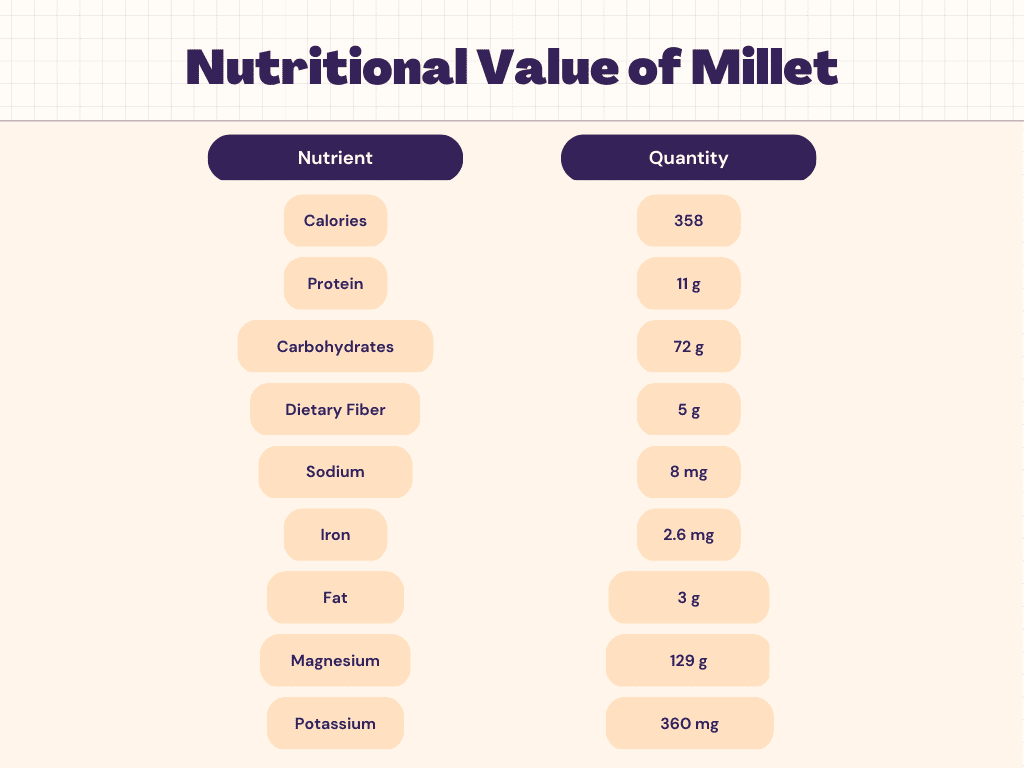
Nutritional Facts of Millet
Carbs In Millet
Millet is a rich source of carbohydrates, with about 72 grams of total carbohydrates per 100 grams of cooked grain. This makes it an important food for people looking to maintain a balanced diet, as carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. The carbohydrates in millet are complex, meaning that they are slowly absorbed by the body and provide a sustained source of energy. Additionally, millet is a good source of fiber, with about 5 grams of fiber per 100 grams of cooked grain. Fiber helps to slow the digestion of carbohydrates and can help to regulate blood sugar levels, making millet a good food choice for people with diabetes or blood sugar concerns. Overall, the carbohydrates in millet provide important nutrients and energy that support overall health and well-being.
Protein In Millet
Millet is also a good source of protein, with about 11 grams of protein per 100 grams of cooked grain. Protein is an essential nutrient that is important for building and repairing tissues in the body, as well as producing enzymes and hormones. It also helps to regulate metabolism and support a healthy immune system. The protein in millet is considered a “complete protein,” meaning that it contains all of the essential amino acids that the body needs but cannot produce on its own. This makes millet a valuable food for people looking to increase their protein intake, especially those who follow vegetarian or vegan diets. Whether you are looking to support muscle growth, repair, or overall health, the protein in millet is an important nutrient to include in your diet.
Health Benefits Of Millet
Millet is a nutritious food that offers several health benefits, particularly for people with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), diabetes, thyroid problems, and those looking to lose weight. Here are some of the ways in which millet can support these health concerns:
- PCOS: Millet is a low-glycemic food, which means that it has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. This makes it a good food choice for people with PCOS, as elevated insulin levels are a common problem in this condition. Check our PCOS Plans here.
- Diabetes: Millet’s low glycemic index and high fiber content make it a good food choice for people with diabetes. It can help to regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall glycemic control. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
- Thyroid: Millet is a good source of magnesium, which is important for thyroid function. A lack of magnesium can lead to an underactive thyroid, so including millet in your diet can help to support thyroid health. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
- Weight loss: Millet is a low-fat, high-fiber food that can help to promote feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake. It is also a good source of protein, which can support weight loss by helping to build and repair muscle tissue. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
Overall, millet is a nutritious food that can offer numerous health benefits, particularly for people with PCOS, diabetes, thyroid problems, and those looking to lose weight. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine how millet may fit into your individual health needs.
Vitamins & Minerals in Millet
In addition to its high levels of carbohydrates, protein, and fiber, millet is also a good source of several essential vitamins and minerals. Here is a list of some of the key vitamins and minerals found in millet:
- Magnesium: Magnesium is important for many bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, heart health, and regulating blood sugar levels.
- Phosphorus: Phosphorus is important for strong bones and teeth, as well as energy metabolism and cell growth.
- Iron: Iron is important for the production of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood.
- B-complex vitamins: Millet is a good source of several B-complex vitamins, including niacin, thiamin, and riboflavin. These vitamins are important for energy metabolism, as well as brain and nervous system function.
- Manganese: Manganese is a trace mineral that is important for bone health, wound healing, and antioxidant function.
- Zinc: Zinc is important for immune system function, wound healing, and taste perception.
These are just a few of the key vitamins and minerals that can be found in millet. It is important to remember that the actual nutrient content of millet can vary depending on the type of grain and the cooking method used. Nevertheless, millet is a nutrient-rich food that can provide important vitamins and minerals to support overall health and well-being.
The Bottom Line
Millet is a nutritious grain that is rich in carbohydrates, protein, fiber, and several essential vitamins and minerals. It has a low glycemic index, making it a good food choice for people with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and diabetes, and its high fiber content helps to regulate blood sugar levels. Millet is also a good source of magnesium, phosphorus, iron, and B-complex vitamins, as well as manganese and zinc. Additionally, its low-fat, high-fiber, and high-protein content make it a good food choice for people looking to lose weight. Overall, millet is a versatile and nutritious food that can provide important nutrients and support overall health and well-being.
Faqs
How much Millet can I eat in a day?
The amount of millet that you can eat in a day will depend on several factors, including your age, sex, weight, and activity level. However, as a general guideline, it is recommended to aim for 1 to 2 servings of whole grains per day, with each serving being around 1/2 to 3/4 cup of cooked millet. This will provide approximately 45-135 grams of carbohydrates, 6-20 grams of protein, and 2-6 grams of fiber, depending on the serving size.
It is also important to consider your overall diet and the other foods that you are eating, as well as any health conditions or restrictions you may have. For example, people with diabetes or who are trying to lose weight may need to limit their portion sizes or choose lower-carbohydrate options.
It is always best to speak with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized recommendations on how much millet, or any other food, is appropriate for you and your specific needs.
Should I eat Millet before or after exercise?
Whether you should eat millet before or after exercise depends on the type and intensity of the exercise, as well as your personal preferences and goals.
For lighter, less intense exercise such as a leisurely walk or yoga class, eating a small serving of millet a few hours before exercise may provide you with a steady supply of energy. Millet is a slow-digesting grain, which means that it will provide you with a slow and sustained release of energy throughout your workout.
For more intense or longer-duration exercise, such as a long-distance run or a weightlifting session, eating millet after exercise may be a better option. Consuming a serving of millet after exercise can help to replenish glycogen stores in the muscles, which can support recovery and muscle growth. Additionally, millet’s high protein content can help to repair and build muscle tissue.
Ultimately, the best time to eat millet before or after exercise will depend on your individual needs and preferences. Some people may find that eating millet before exercise provides them with the energy and focus they need to perform at their best, while others may find that eating millet after exercise supports their recovery and muscle growth. Experimenting with different timing and portion sizes can help you determine what works best for you.
What are the benefits of Millet?
Millet is a highly nutritious grain that offers a variety of health benefits. Some of the key benefits of millet include:
- Low glycemic index: Millet has a low glycemic index, which means that it is absorbed into the bloodstream slowly, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of insulin spikes.
- Rich in fiber: Millet is a good source of fiber, which is important for digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and supporting weight management.
- High in protein: Millet is a good source of plant-based protein, making it a great food choice for people following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- Gluten-free: Millet is naturally gluten-free, making it a suitable food choice for people with celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
- Good source of vitamins and minerals: Millet is a good source of several essential vitamins and minerals, including magnesium, phosphorus, iron, and B-complex vitamins, as well as manganese and zinc.
- Supports heart health: Millet’s high fiber, low-fat, and low-sodium content can help to reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Promotes digestive health: The high fiber content of millet can support digestive health and regularity.
- Supports weight management: Millet’s low-fat, high-fiber, and high-protein content makes it a good food choice for people looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight.
Overall, millet is a versatile and nutritious grain that offers a variety of health benefits. Including millet in your diet can help to support overall health and well-being, as well as provide important vitamins and minerals to support specific health goals and conditions.
What is the best time to eat Millet?
The best time to eat millet can vary depending on your individual needs and preferences. However, here are a few general guidelines:
- Breakfast: Millet can be a nutritious and filling option for breakfast, especially when paired with other healthy ingredients like fruit, nuts, and seeds.
- Lunch: Millet can be a great addition to a balanced lunch, either as a side dish or as the main ingredient in a salad or grain bowl.
- Dinner: Millet can be used as a tasty and nutritious alternative to rice or pasta for dinner, especially when paired with vegetables and a lean protein source.
- Snacks: Millets can also be used to make healthy snacks, such as baked millet balls or crunchy millet crackers.