A 2000 calorie diet plan is popular among those who wish to lose a few kilos while still gaining all their needed nutrition because it gives you enough energy for the day without lowering your calorie intake, so you do not feel deprived. In any case, it does not treat extreme restriction but targets the control of nutrient-dense portions and food choices. This diet is designed to adopt a healthy and safe approach to the environment. Thirdly, since flexibility is incorporated into this diet, you can modify it according to your age, activities, and even the weight you desire to achieve. Hence, the plan will guide you to an excellent aim, be it losing a few pounds or maintaining fitness.
How to Follow a 2000 Calorie Diet for Weight Loss?
To stick to a 2000 calorie diet plan, you will have to allocate your calories to three meals and two snacks a day. Ensure that every meal contains lean proteins, healthy fats, and carbohydrates. Remember to use only complex carbohydrates with fruits and vegetables to avoid getting hungry easily. Such foods include chicken, fish, quinoa, avocados, etc. For example, foods with high fiber intake include whole grains and legumes, which help keep digestion movement, thus making one feel full for a longer time and avoiding overeating calories. Besides, using advanced meal planning and a daily calorie intake calculator, reading nutrition labels, and cooking at home makes calorie intake relatively easier. Research shows that eating a balanced mix of nutrients helps protect your muscle mass while your body burns fat.
Meal Plan for 2000 Calorie Diet
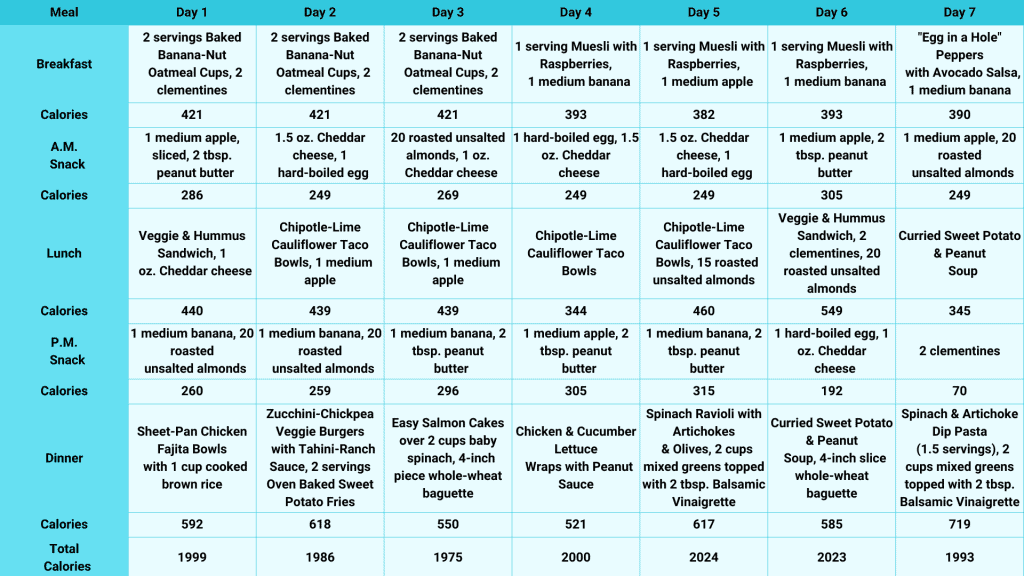
A well-rounded 2000 calorie meal plan ensures you receive the right nutrients without exceeding your calorie limit. Below is a balanced 7-day meal plan that includes breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks to help you stay on track and you can also buy weightloss diet plan for further assistence.
Day 1
Breakfast
- Baked Banana-Nut Oatmeal Cups: 2 servings of these nutritious oatmeal cups are packed with fiber and healthy fats.
- Clementines: 2 small clementines add a vitamin C boost.
Lunch
- Veggie & Hummus Sandwich: A veggie-filled sandwich with hummus for a plant-based protein hit.
- Cheddar Cheese: Add one oz. of cheddar cheese for extra calcium and flavor.
Dinner
- Sheet-Pan Chicken Fajita Bowls: Grilled chicken, bell peppers, and onions over 1 cup of cooked brown rice make this a well-balanced meal with lean protein and complex carbs.
Snacks
- Apple Slices with Peanut Butter: A medium apple with 2 tbsp. Peanut butter adds healthy fats and fiber.
- Banana & Roasted Almonds: A banana with 20 roasted unsalted almonds rounds out your daily nutrition.
Day 2
Breakfast
- Baked Banana-Nut Oatmeal Cups: 2 servings with two clementines.
Lunch
- Chipotle-Lime Cauliflower Taco Bowls: This flavorful bowl features cauliflower as a low-calorie substitute for grains, paired with a tangy chipotle-lime dressing.
- Apple: Add a medium apple on the side for added fiber.
Dinner
- Zucchini-Chickpea Veggie Burgers: These plant-based burgers pack protein and fiber and are served with tahini-ranch sauce.
- Oven-Baked Sweet Potato Fries: A serving of these nutrient-dense fries provides vitamins A and C.
Snacks
- Cheddar Cheese & Hard-Boiled Egg: 1.5 oz. of cheddar cheese and a hard-boiled egg make for a satisfying protein-rich snack.
- Banana & Almonds: A banana and 20 unsalted roasted almonds for extra energy.
Day 3
Breakfast
- Baked Banana-Nut Oatmeal Cups with two clementines.
Lunch
- Chipotle-Lime Cauliflower Taco Bowls with a medium apple.
Dinner
- Easy Salmon Cakes served over 2 cups of baby spinach for a heart-healthy omega-3-packed meal.
- Whole-Wheat Baguette: Pair with a 4-inch slice of whole-wheat baguette for added fiber and whole grains.
Snacks
- Almonds & Cheddar Cheese: Combine 20 roasted almonds with 1 oz. of cheddar cheese for a snack with healthy fats and protein.
- Banana & Peanut Butter: A banana with 2 tbsp. Of peanut butter for a filling snack.
Day 4
Breakfast
- Muesli with Raspberries: 1 serving of fiber-packed muesli topped with raspberries, plus a banana for added sweetness.
Lunch
- Chipotle-Lime Cauliflower Taco Bowls for a flavorful, low-calorie meal.
Dinner
- Chicken & Cucumber Lettuce Wraps: These light wraps, served with peanut sauce, offer a healthy balance of protein and fats.
Snacks
- Hard-Boiled Egg & Cheddar Cheese: A hard-boiled egg with 1.5 oz. of cheddar cheese for a protein boost.
- Apple & Peanut Butter: A medium apple with 2 tbsp. Of peanut butter.
Day 5
Breakfast
- Muesli with Raspberries: 1 serving with a medium apple.
Lunch
- Chipotle-Lime Cauliflower Taco Bowls with 15 roasted unsalted almonds.
Dinner
- Spinach Ravioli with Artichokes & Olives: This Mediterranean-inspired dish is rich in fiber and antioxidants.
- Mixed Greens Salad: Topped with 2 tbsp. of balsamic vinaigrette.
Snacks
- Cheddar Cheese & Hard-Boiled Egg: 1.5 oz. Cheddar cheese and a hard-boiled egg.
- Banana & Peanut Butter: A banana with 2 tbsp. Peanut butter.
Day 6
Breakfast
- Muesli with Raspberries: 1 serving with a medium banana.
Lunch
- Veggie & Hummus Sandwich: Filled with fresh vegetables and hummus.
- Clementines & Almonds: 2 clementines with 20 roasted almonds.
Dinner
- Curried Sweet Potato & Peanut Soup: This creamy, plant-based soup balances healthy fats and carbohydrates.
- Whole-wheat baguette: 1 (4-inch) slice.
Snacks
- Apple & Peanut Butter: A medium apple with 2 tbsp. Of peanut butter.
- Hard-Boiled Egg & Cheddar Cheese: 1 hard-boiled egg with one oz. of cheddar cheese.
Day 7
Breakfast
- “Egg in a Hole” Peppers with Avocado Salsa: A protein-packed breakfast with healthy fats from avocado.
- Banana: A medium banana on the side.
Lunch
- Curried Sweet Potato & Peanut Soup: A repeat of the delicious, nutrient-dense soup.
Dinner
- Spinach & Artichoke Dip Pasta: 1.5 servings of this creamy pasta dish made with nutrient-rich spinach and artichokes.
- Mixed Greens Salad: Topped with balsamic vinaigrette.
Snacks
- Apple & Almonds: A medium apple with 20 roasted almonds.
- Raspberries & Dark Chocolate: 1 cup of raspberries with one oz. of dark chocolate for a sweet treat.
This plan provides a wide variety of foods that are not only tasty but also nutritious, making it easier to stick to your 2000 calorie diet plan for weight loss and may also be transformed into 3000 calorie diet plan if someones requirements are more.
Can a 2000 Calorie Diet Plan Help You Lose Weight?
Yes, a 2000 calorie diet plan for weight loss can help you lose weight, as it depends entirely on how you balance your meals. For example, if you eat low calorie foods and consume fewer calories than you burn, then you will lose weight. Indeed, for many people, 2000 calories give them a slight calorie deficit, especially for highly active individuals. Similarly, nutrient-dense but low-calorie food selection, such as vegetables, lean meats, and whole grains, keeps you full without overeating. Again, the result is age, gender, and activity level dependent upon those individuals. Thus, by paying attention to portion size and removing those processed, high-calorie products from the table, you can stay less and have a more constant and sustainable balance.
Foods to Eat on a 2000 Calorie Diet Plan
A 2000 calorie diet plan for weight loss is just what makes it suitable for you to choose as it satisfies you with food that fulfills the nutritional demand. They must be packed highly with proteins, healthy fats, fiber, and all other essential vitamins to help you through weight loss and health benefits. So here’s a list of the best food items for your plan:
1. Lean Proteins
The plus side of lean proteins and protein rich foods is that they help repair your muscles and they boost your metabolism, so you’ll be full all day long instead of binge eating.
- Chicken Breast: Low in fat and with a wealth of protein, chicken breast makes excellent lean proteins that contribute to the building of your muscles while you lose a few pounds.
- Turkey: Another lean alternative, turkey contains all the essential amino acids and is lower in calories and fats than red meat.
- Fish: Salmon, cod, and Tuna contain omega-3 fats, which are anti-inflammatory but heart-benefiting and help the brain function properly. This nutrient-enriched salmon is great for getting healthy fat along with protein.
- Tofu: A plant-based protein prepared from soy, it is rich in calcium and iron and thus an excellent vegetarian and vegan food choice. Though low in calories, it is rich in protein, hence not suitable for use in body mass losses without damaging muscular tissue.
2. Whole Grains
Whole grains contain slow-digesting carbohydrates that provide a sustained energy release in the body and promote healthy digestion.
- Brown Rice is very rich in fiber and also full of essential vitamins and minerals. It keeps the system running well and going for a long period, thus preventing overeating.
- Quinoa is a complete protein and a essential part of Virat Kohli diet plan, because it is a source of all nine of the essential amino acids. It is also high in fiber, iron, and magnesium, making it a good substitute for rice.
- Oats contain soluble fiber, which lowers cholesterol and makes a person feel full. They are superb for breakfast or as a snack.
3. Fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are highly rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which contribute to health and help with weight loss with a simple diet plan.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, Kale, and Arugula are low in calories but are a great source of vitamins A, C, and K, fiber, and more. They make good fillers without adding extra calories.
- Broccoli: This vegetable is very fiber-rich and contains essential vitamins like vitamin C and folate. It is helpful for digestion and makes one feel full, which helps one lose weight.
- Berries, strawberries, Blueberries, and Raspberries are low-calorie and full of antioxidants and fiber. They reduce inflammation, work against diseases, and they sure help satisfy your need for some sweetness.
- Sweet potatoes are starchy vegetables that are a high-nutrient source of fiber, vitamins A and C, and potassium. They act as an ideal healthy, low-calorie alternative for diets.
4. Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are always good since they help you consume fat-soluble vitamins, keep your brain, heart, and body healthy, and keep you fuller for longer. These are great options to include in the 30 30 30 rule for weight loss.
- Avocados, rich in monounsaturated fats and fiber, help you feel full and support heart health; they also contain key nutrients such as potassium.
- Nuts -Almonds and walnuts are nutrient-dense foods that provide healthy fats, fiber, and proteins. They are also great sources of nutrients for the brain and heart, with almonds being rich in vitamin E and walnuts providing omega-3 fatty acids.
- Seeds contain the right nutrients, including omega-3s, proteins, and fiber. They are also taken for minimal inflammation and filling. Chia Seeds, Flaxseeds, and Pumpkin Seeds are among these.
- Olive oil: High in monounsaturated fats, olive oil is a great healthy choice for cooking and dressing salads. Its antioxidants protect against oxidative damage and enhance overall health.
5. Milk and milk alternatives
Dairy and plant-based products do offer calcium, protein, and most of the vitamins that contribute to bone health and muscle repair and are great as weight loss drinks.
- Greek Yogurt is rich in proteins and probiotics, which are dangerous for digestive health. It also keeps you fuller. Use low-fat versions to keep calorie intake to a minimum but retain nutrients.
- Low-fat milk contains calcium and vitamin D. It keeps the body’s bones in good health while providing some proteins without excess fat.
- Milk: Almond milk is the next best alternative for those who can’t consume lactose. It has low-calorie content but is rich in calcium and vitamins.
Foods to Avoid on a 2000 Calorie Diet Plan
A 2000 calorie diet will help you lose or maintain your weight to the best; to get maximum benefits from a diet, you should restrict your diet to foods with little nutritional value but a high empty calorie count. Such foods tend to make you indulge and interfere with your ability to stay within your caloric intake, defeating the whole point of doing the diet. Below is a list of foods that you should avoid while on a 1000 calorie diet plan for weight loss.
1. Processed foods
Processed foods attempt to contain empty calories, so they provide a large number of calories in very little actual nutrition. Added sugars, unhealthy fats, and preservatives are inherent in foods like these. This can quickly lead to weight gain and numerous health problems.
- Candy: Very high sugar added and provides almost nothing in the way of nutrition. You get that, but all that sugar brings some pretty nasty floods of insulin and intensified cravings to you, making it pretty darn tough to stick to your diet.
- Soda: While traditional soda has only added sugars and empty calories, the high consumption of soda leads to weight gain, and everything gained by drinking it can supposedly confer risks to obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Fast Food: Fast food is very high in calories, fats, and sodium, with an adjunct of little to no nutritional value. Foods such as burgers, fries, and fried chicken add calorie intake but do not contribute to the body’s vitamin and mineral intake that it needs to shed weight.
2. Processed Grains
The more processed the grains, the more bran and germ are removed. The nutritious components of the grain have thus been lost, and such foods become low in fiber as well as other much-needed nutrients. Such foods also cause rapid rises in blood sugar.
- White Bread: White bread is made from refined flour, which has lost much of its fiber. The lack of fiber means that it is digested quickly, causing a rapid spike in blood sugars that will again leave the person hungry almost instantly.
- Pasta: White pasta is manufactured from refined grains with little fiber and protein. It is, hence, crucial in keeping the individual full and satisfied. This might make it hard to overdo eating but could also make it almost impossible to be in a calorie deficit.
3. Processed Meats
Processed meat refers to meat that contains unhealthy fats, sodium, and a variety of preservatives. Diets high in such meat have been linked to higher risks of medical conditions like heart disease, cancer, and obesity.
- Bacon is also a source of saturated fat and calories. This means that it can contribute to weight gain and raise cholesterol levels in the body, potentially threatening the heart.
- Processed Sausages: Sausages are extremely calorie-dense and contain unhealthy fats. Many sausages also contain added sugars and fillers, increasing calorie counts without providing nutritional value.
4. Sweetened Beverages
Sweet drinks are another source of added sugars and calories. Let’s assume that the maximum daily calorie intake is 2000 calories. Consuming those liquids during the day would be hard while keeping calorie consumption at that level. As for solid foods, a person gets sated while being digested. Such feelings of satiety are not given with sweet drinks; thus, they are overconsumed throughout the day.
- Fruit juices: Although fruit juices appear to be a healthy beverage, they contain as much sugar as soda. Since they do not carry the fiber content from whole fruits, they are rather incapable of suppressing hunger and can make you eat more calories than you should.
- Sugary Teas and Coffees: Bottled teas, coffee drinks, and most other liquid beverages are filled with added sugars and syrups, turning what could have been a healthy drink into a calorie bomb.
5. Alcohol
Alcohol is also extremely caloric, and it doesn’t give your body much nutritional benefit. The results really do add up quickly, as your 2000-calorie limit is far surpassed without giving your body the nutrients it needs.
- Beer and Cocktails: Beer and cocktails are extremely calorie-dense drinks, though they also hinder your ability to make judgments and cause you to consume far more than you should. Heavily drinking is likely to contribute to gaining weight and poor metabolic health.
Benefits of Following a 2000 Calorie Diet Plan
A 2000 calorie diet plan ensures that most people consume adequate calories to meet their daily energy needs. This is the most frequently used “calorie level” when selecting labels on food product nutrition contents; this calorie consumption can either be kept at a level or gradually decreased according to age, levels of activity, and metabolism by measuring it with BMR calculator. According to research and proven health facts, some of the major benefits of following such a diet are as follows.
1. Helps in Gradual Weight Loss
A 2000 calorie meal plan implies smooth weight loss if supplemented by exercise. With help of food calorie calculator and proper calorie supplements and nutrient-dense foods, the body tends to utilize stored fat for energy.
- Caloric Deficit: To lose fat, the body needs to burn more calories than it consumes. A 2000-calorie diet for some people who require more calories per day can be quite balanced in producing a caloric deficit, thus achieving fat loss without extreme hunger and fatigue. Many studies have shown that gradual and slow weight loss is more likely to become long-term and avoid the above vicious circle of yo-yo dieting.
2. Guarantees Nutrient Balance
A 2000 calorie meal plan involves a good balance of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—and micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals, ensuring that the body gets all its required nutrients to function optimally, gain energy, and prevent diseases.
- Macronutrient mix: The approximate level for a diet in this calorie range is 45% to 65% from carbohydrates, 10% to 35% from proteins, and 20% to 35% from fat. These measures detail how energy production, muscle repair, and brain functions are undertaken.
- Micronutrients: A 2000-calorie diet adequate in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains should provide plenty of vitamins A, C, and E, along with minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which are helpful to support a healthy immune system.
3. Boosts Energy
It gives the body just the right amount of calories and the correct nutrient profile; one would have a boosted energy level throughout the day. Most people, in actuality, experience less fatigue and avoid that mid-afternoon slump wherein they already fell asleep without having an attack of a snooze button because they are constantly fueling their bodies with healthy whole foods. Unlike fad diets that severely reduce calorie intake and cause spats of low energy, this 2000 calorie meal plan provides a steady stream of complex carbohydrates and healthy fats, therefore helping to increase concentration, productivity, and endurance in the workplace, at the gym, or in life.
4. Reduces Risk of Chronic Diseases
A second vital advantage of a 2000 calorie meal plan is that the risk of chronic conditions, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease, can be minimized. A balanced intake of nutrient-rich food often prevents the abnormal increase of sugar levels in blood, cholesterol, and blood pressure rates.
- Obesity: Obesity is avoided in those following a calorie-controlled diet of whole, unprocessed foods since they abhor the overeating associated with dieting-the number one risk factor in most chronic diseases.
- Diabetes: Complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats will minimize the risk of high blood sugar levels, which, on a 2000 calorie meal plan, will minimize the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Heart Health: A food with healthy fats, low saturated fat content, and very high dietary fiber, hence heart-friendly. Even the LDL cholesterol level came down with a consistent 2000 calorie diet, and cardiovascular function improved.
5. Flexible and Sustainable
One of the nice flexibility benefits of this diet plan is its 2000-calorie limit as it demands extreme food restrictions, and eliminations are not necessary, which makes it very easy to stick to in the long run. With this diet plan, you can eat any food you want within your calorie limit. This way, you avoid diet fatigue and develop an aversion to meals.
- Long-Term Sustainable: Due to its simplicity and flexibility, this diet is sustainable, and people maintain it over a long period without feeling frustrated or deprived. As long as all food groups are incorporated in moderation, such a diet can be very comfortably followed for more healthy long-term health outcomes.
6. Supports Healthy Weight Maintenance
A 2000 calorie meal plan is appropriate for people who hope not to lose weight but achieve a healthy body weight. They have adequate calories to satisfy their daily energy needs but no extra calorie mass that causes unwanted weight gain.
- Healthy Metabolism: When a diet is combined with regular physical activity, it prevents a decrease in metabolism, which is common and associated with too-severe diets. Overall, metabolism is significant in preventing swinging weights and disease-related dangers.
Why Are 2000 Calories Often Considered Standard?
Generally, the 2000 calorie meal plan standard is accepted because it reports the average number of calories a majority of adults must consume daily to preserve their energy and bodily functions without gaining weight, as a standard value is used in food labels and dietary guidelines across countries. In simple words, calories measure the energy the body needs to perform the most basic functions, such as breathing, digesting, and keeping a normal body temperature. They also power ordinary activities like walking, working, or walking across the block to get some exercise. Nutrition experts recommend an average 2000-calorie mark based on studies and data from research on various population groups’ energy needs.
But again, this isn’t a “one size fits all” situation; age, gender, activity level, and metabolism all impact one’s caloric needs on any given day. For instance, younger people and those who are more active may need more than 2000 calories, whereas older or less active people will need fewer. In general, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans report that women need about 1800-2200 calories a day, while men may require about 2200-2800 calories, depending on their level of physical activity. So, while a 2000-calorie number is a useful guideline for the average adult, individual needs should always be considered to achieve optimal health.
Who Should Follow a 2000 calorie diet plan?
A 2000 calorie meal plan is suitable for those looking to maintain or lose weight slowly. Caloric intake at this level is perfectly suited for moderately active people. Those who work out lightly to moderately, say walking or cycling or hitting the gym a couple of times a week, will be just fine with this caloric intake level. If someone’s lifestyle is moderately active, such as light to moderate activity, but not highly active and not vigorously exercising every day, a 2000 calorie meal plan would likely keep that person at the weight that they have now. It would give you just enough energy to do daily activities without gaining extra weight. It provides enough calories to keep your body fueled without overdoing it, so enjoy the food variety in moderation. If you’re trying to lose weight, a 2000-calorie diet may work well as it creates a moderate caloric deficit and slowly loses fat while leaving you feeling satisfied at meals.
Expert Review on 2000 Calorie Diet Plan
According to Dr. Ayush, a registered nutritionist with extensive expertise in nutrition and dietary practices, following a 2000 calorie meal plan gives those who intend to lose weight an ideal chance with zero sacrifice of nutritional values. He notes that the key factor for this diet is to focus on whole foods, which are normally less processed and rich in lean proteins, thereby supporting muscle regeneration and healthy fats, which are positive for health. Such strategic focus helps users neither deviate from their goal path nor feel deprived or dissatisfied. Again, it should be emphasized once more that portion control, along with proper meal planning, is a key way to ensure that you keep your daily calorie intake within manageable limits. This ensures that you remain within your allowed calorie intake, which will then help you take full advantage of your weight loss goals.
References
“Calories – StatPearls.” n.d. NCBI. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499909/.
“Calories – StatPearls.” n.d. NCBI. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499909/.
“Calories – StatPearls.” n.d. NCBI. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499909/.
FAQs
1. How can I get 2000 calories per day?
Achieving a 2,000-calorie intake requires a balanced meal plan with a variety of macronutrients. You can divide the calories across three meals (about 500-600 calories per meal) and two snacks (around 200-300 calories each). For instance, you can have oatmeal with peanut butter for breakfast, a grilled chicken salad for lunch, and baked salmon with sweet potatoes for dinner. Snacks could include Greek yogurt with berries or nuts. Including a mix of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbs will help you reach your calorie target in a nutritious way.
2. How many kg is 2000 calories?
In terms of body weight, 1 kilogram is equal to 7,700 calories. So, consuming 2,000 calories equates to about 0.26 kg. However, whether this leads to weight gain or loss depends on your overall daily calorie balance, activity level, and metabolism.
3. How many grams in a 2,000-calorie diet?
The number of grams per macronutrient in a 2,000-calorie diet depends on your macronutrient breakdown. A diet comprising 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fats translates to around 200 grams of carbohydrates, 150 grams of protein, and 67 grams of fat daily.
4. Is 2000 calories a good diet?
A 2,000-calorie diet is often considered standard for many adults and can help maintain or lose weight depending on your activity level, age, and goals. It provides enough nutrients for most people, but individual needs may vary.
5. How to eat 2,000 calories a day?
To consume 2,000 calories per day, spread your intake across nutrient-dense meals and snacks. A balanced meal plan with lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can help. For example, meals could consist of 3 ounces of protein like chicken, paired with complex carbs like whole wheat pasta and healthy fats such as avocado.