A vegan meal plan excludes all types of meat, fish, dairy, eggs, and honey, with other forms of derivatives of animal byproducts, such as gelatin, whey, or casein, which are also avoided in a vegan diet plan. Many have this recent urge to try out the plant-based lifestyle for several reasons. First and foremost, for ethical beliefs or environmental concerns or perhaps due to health considerations. It would need more whole plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and grains. This vegan diet plan for beginners is quite rich in natural fiber, antioxidants, and vitamins. It is so beneficial to improving cardiovascular health, supporting weight management, and perhaps lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes.
Sufficient levels of other nutrients, such as calories, calcium, iron, and B12, need to be provided by those embracing a vegan diet meal plan. Proper planning will ensure that a vegan diet will receive all the nutrients that can lead to a healthy lifestyle.
What is a Vegan Diet?
A vegan meal plan would be a pattern of eating that is plant-based and where every product from animals was excluded, such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy, and some of the less obvious ingredients, such as gelatin, whey, casein, and honey. The core composition of a vegan diet plan for beginners is composed of entire, nutrient-dense plant foods. These are highly rich in vitamins, minerals, fibers, and antioxidants, functioning together for better bodily health and the prevention of diseases.
1. Fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are very low calorie foods and rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Berries are the fruits, and spinach and kale are the vegetables with high antioxidants that help fight inflammation and oxidative stress associated with chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease. The study finds high intakes of fruits and vegetables to be associated with risk and causes of mortality from cardiovascular diseases.
2. Nuts and Seeds
Other primary sources for a vegan diet come in nuts and seeds, further contributing to healthy fats and protein intake, besides their essential micronutrients. Most are part of the almonds, chia seeds, or flaxseeds, each containing omega-3 fatty acids. They have been proven to be very important for heart health. As the uptake from fish is included in a non-vegan diet, plants can replace them with a vegan diet plan. The nuts and seeds are highly protein rich foods because their magnesium and zinc content is quite high.
3. Beans
Legumes like beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas will fill in the protein and fiber that a plant-based diet needs. Since this was filled by the inclusion of animal products into diets, these legumes will now fill in that plant-based source of protein content. Legumes also contain iron, another mineral used to transport oxygen through the blood. For better iron absorption, include legumes with vitamin C-rich foods like tomatoes or citrus fruits.
4. Whole grain
Brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat are whole grains and fall under complex carbohydrates, providing energy to the body for an even longer time. Most of the dietary fibers are found in whole grains. It maintains the functions of the gut intact while preventing any type of change in blood sugar levels, thereby reducing the chance of getting into type 2 diabetes. Vitamin B, which exists in whole grains, catalyzes energy metabolism and the proper functioning of the brain. Research observed that the outcome was that body weight is lower and associated with less abdominal fat.
5. Plant-based dairy alternatives
As milk is not a component of any food that a vegan would consume, other plant-based ‘milk’ equivalents like soy, almond, oat, and many more are also included. These, to a large extent, are formulated to be prepared with calcium, vitamin D, and B12. Therefore, they are integral to encouraging healthy bones and preventing nutrient deficiencies that would otherwise be obtained from animal products.
6. Sprouted or fermented plant foods
Examples include tempeh, sauerkraut, and miso foods that are sprouted and fermented and promote the gut’s health as they consist of probiotics-good bacteria that help digestion and increase the immune system’s efficiency. As stated in a research study that has been conducted, probiotics contribute to a healthy gut microbiome, which consequently lowers inflammation and helps one fight illness and disease better.
7. Vegetable Oils
Vegetable oils, comprising olive, avocado, and coconut, are highly rich in healthy fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These oils are highly essential for fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. In addition, vegetable oils are an energy source, and oils such as olive oil are well-known for their cardiovascular benefits. Individuals consuming Mediterranean diets with high intakes of olive oil have lesser heart disease and stroke rates.
A well-designed vegan diet meal plan is also associated with many health benefits, including a lower risk for heart disease, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and some forms of cancer. The high fiber content in plant food is useful in digesting food and assisting one in losing weight. Additionally, research indicates that people on a plant-based diet or vegan meal plan have a significantly lower risk for chronic diseases than omnivorous diets. All these require vegans to ensure they obtain essential nutrients, like vitamin B12, iron, and calcium, through fortified foods or supplements, and for one, opt to Buy Weightloss diet plan.
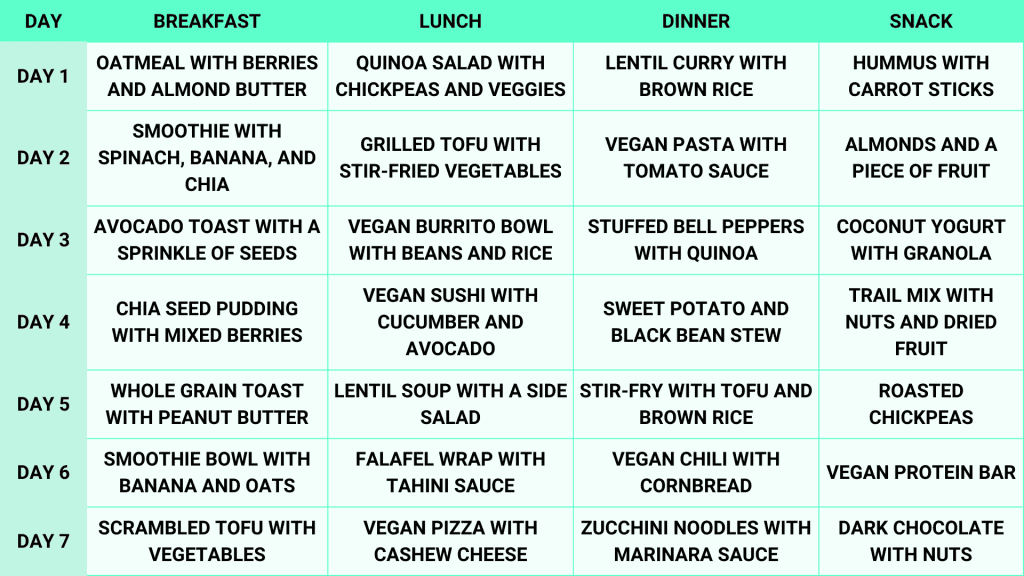
7 Days Vegan Diet Meal Plan
A well-planned vegan meal plan can help you meet your nutritional needs while enjoying a variety of plant-based dishes. Here’s a 7-day vegan meal plan to get you started:
Day 1
- Breakfast: Oats with berries and chia seeds
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with olive oil dressing
- Dinner: Steamed fish with broccoli
- Snacks: Almonds and green tea
Day2
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach
- Lunch: Lentil soup with whole-grain bread
- Dinner: Paneer stir-fry with mixed vegetables
- Snacks: Apple slices with peanut butter
Day 3
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with walnuts
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with chickpeas
- Dinner: Grilled tofu with roasted veggies
- Snacks: Handful of mixed nuts
Day4
- Breakfast: Smoothie with banana, protein powder, and almond milk
- Lunch: Whole-wheat chapati with vegetable curry
- Dinner: Grilled salmon with asparagus
- Snacks: Carrot sticks with hummus
Day 5
- Breakfast: Poha with peanuts and green chilies
- Lunch: Chicken tikka with cucumber salad
- Dinner: Lentil curry with brown rice
- Snacks: Cottage cheese cubes
Day6
- Breakfast: Chia pudding with berries
- Lunch: Paneer tikka with mixed greens
- Dinner: Grilled shrimp with sautéed spinach
- Snacks: Walnuts and herbal tea
Day 7
- Breakfast: Vegetable omelette
- Lunch: Millet khichdi with yogurt
- Dinner: Baked chicken with roasted sweet potato
- Snacks: Fresh fruit salad
How to Start Following a Vegan Diet Plan?
Transitioning to a vegan diet meal plan is an exciting but serious lifestyle move that calls for careful planning if one is to gain maximum nutrition. A vegan diet plan for beginners excludes all food products of animal origin. That means meat, dairy products, and eggs are excluded, focusing on plant-based food and weight loss drinks. In this kind of vegan diet plan, the food must be well-balanced, especially in terms of protein, vitamins, and minerals, because most of these are tied up with animals.
1. Gradual transition to plant-based diet
Introducing a vegan diet plan for beginners is something that should be easy. Gradually introducing it is, in fact, the best approach. Do not try to quit all animal products at once. Instead, include one or two weekly plant-based meals to replace existing ones. This gradual process allows your body and palate to get accustomed to the new foods, thus making the change less scary. For example, you may start by substituting cow’s milk with almond or oat milk, then gradually avoid meat and replace it with plant-based sources of proteins, such as lentils, beans, or tofu.
2. Discover plant-based alternatives
A vegan diet meal plan is one of the secret formulas to success is finding plant-based versions of your favorite foods. This goes hand-in-hand with more vegan products on the shelves, making it easy to substitute animal-based ingredients with plant-based ones without compromising taste. Concoctions such as vegan cheese, almond milk, and plant-based meats make the transition smoother while keeping some elements of familiar flavors and textures intact. Adding these alternatives to your meals creates opportunities for sticking to a vegan diet while at the same time exploring new flavors and textures.
3. Meal planning on a vegan diet
Proper planning of meals, along with a food calorie calculator ensures a balanced diet. A weekly meal plan can be developed to integrate all the macro and micro requirements using plant-based foods. This would mean that every meal with the right mix of vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds would guarantee nutrient adequacy. Some plant-based sources of protein include tempeh, seitan, or quinoa. A few fortified foods can be included, such as plant-based milk for calcium and vitamin D. Food planning should be done regularly to avoid wasting time and minimize the risk of deficiencies in essential nutrients such as vitamin B12 and iron for weight loss with a simple diet plan.
4. Stocking up the pantry with staples
Stock your pantry with staples for vegan meals to maintain consistency, and use the various beans, lentils, quinoa, oats, nuts, seeds, and tofu as meal preps. Most meals should include whole grains and legumes as staple ingredients. Nuts, seeds, and health oils like olive or avocado can provide your total allowance for daily fat intake, but you can also use a daily calorie intake calculator to measure it. These readily available items ensure you’re prepared to create balanced and satisfying meals.
5. Nutrition of a Vegan
Before embarking on a vegan meal plan, one is better informed about how to get all the nutrients properly; some nutrients, like vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, become more challenging to obtain from the diet. B12, for example, occurs mainly in animal products, so fortified foods, such as cereals or plant-based milks, or a supplement would be necessary. Supplement with iron when needed through legumes, dark leafy greens, and iron-fortified foods. Vitamin C, in a glass of orange or bell pepper, will enhance iron body absorption.
Who Should Follow a Vegan Diet?
A vegan diet works for people to improve their health condition, reduce environmental impacts, or perfectly fit within ethical beliefs. Vegans steer clear of all products from animals, making it the perfect diet for those concerned about how animals are treated or contributing to carbon footprints. In addition, a vegan diet might benefit specific medical conditions, like heart disease or high cholesterol, since it eliminates saturated fats and cholesterol. A vegan diet can also sometimes benefit overweight people who want to lose weight or people diagnosed with diabetes because it tends to be low-calorie, high in fiber, and nutrient-dense for satiety and balancing blood sugars.
Foods to Eat on a Vegan Diet Plan
A vegan meal plan inspires wholesome, nutrient-rich plant food and general wellness by excluding all animal products. You center your eating on a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and plant-based alternatives to dairy products to ensure you eat a balanced and nourishing diet. In all these categories of food, you get those necessary vitamins, minerals, proteins, and healthy fats, which are very significant to maintaining a healthy lifestyle when on a vegan diet.
1. Fruits
Fruits are some of the most important portions of food in a vegan diet because they highly consist of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The fruits include some human beings like berries, apples, bananas, and citrus fruits, which may enable the provision of a large amount of nutrients needed to provide good proper immune function and for digestion and skin health. The antioxidant fights inflammation and safeguards the human body against the stress caused by oxidation, thus leading to low chances of chronic diseases.
2. Vegetables
There are vegetables full of all the vitamins, minerals, and fiber, thus making them a much-required constituent of a vegan diet. Some offer the best sources of calcium, iron, and vitamin K for solid bones and blood clotting. The raw vegetable group contains crucifers such as broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts full of fiber and anticancer compounds. You can include a variety of vegetables, such as bell peppers, carrots, and sweet potatoes into your diet. You will get a good amount of nutrients.
3. Whole Grains
The complex carbs in brown rice, quinoa, oats, and barley provide whole-day wholesome energy. These whole grains contain a lot of fiber for a healthy digestive system and are especially good for controlling blood sugar spikes. All grains contain B vitamins, a nutrient that helps the body utilize energy and supports cerebral functions. Quinoa is a complete protein because it contains all the nine indispensable amino acids and is, hence, an important protein source for vegan diets.
4. Legumes
Beans, lentils, peas, and chickpeas form the bulk of a vegan diet mainly due to their content. They have full proteins in them and iron. Proteins help repair muscles; they have iron for proper oxygenation around the body. Other advantages lentils and chickpeas provide are fiber content for a good functioning digestive system and ensures a fit size. Legumes, other than providing the body with a good protein source, also provide significant amounts of folate, magnesium, and potassium, which is one of the major contributors to keeping the heart healthy and thus reducing the chance of chronic diseases.
5. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds store good fats, proteins, and other micro-nutrient-dense nutrients. Some nuts and seeds include almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, which are sources of omega-3 fatty acids. These may prove particularly critical for the health of hearts and brains. These are the richest sources of nutrients in antioxidants, fiber, and minerals like magnesium and zinc. A mix of nuts and seeds should be utilized in a vegan diet to get a balanced composition of fatty acids.
6. Plant-based dairy
The most commonly used types of plant-based dairy include almond milk, soy milk, and oat milk. Plant-based dairy is very similar to traditional dairy in nutritional contents, which possess a lot of nutrients that nutritionally are dense. More commonly used additives in these alternative milk are calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12 since these elements are generally more characteristic of animal-based dairy. Soy milk is particularly high in proteins and contains all eight essential amino acids, making it an excellent dairy substitute. Most of the plant-based alternatives to these dairy products, by unfortunate coincidence also tend to fall on the lower side of calorie and fat as compared to their dairy counterparts, thus making them very suitable for a vegan diet.
Foods to Avoid on a Vegan Diet Plan
The vegan diet does not contain any animal-derived products as well as byproducts. Hence, meat and some other obviously observable edibles are excluded in such a diet besides other clearly observable dairy products while some other more sneaky but relatively common hidden animal ingredients are added to most processed foods. It is on this account that identification of whether no animal-based components are included requires scrutiny of food labels and ingredients in a vegan diet.
1. Meat and poultry
Meat and poultry include all cuts of flesh from animals, pork, chicken, lamb, and so on. Philosophically, environmentally, and regarding health, a strictly vegan diet avoids meat entirely. Meat, incidentally, is also one of the leading contributors to saturated fats and cholesterol, both of which directly point to heart diseases; therefore, it has to be one of the first classes of food left behind when opting for a vegan lifestyle.
2. Fish and Seafood
For example, a vegan diet does not include fish and other sea products like shrimp, crab, lobster, and all other creatures in the water. Although it is very popular for its omega-3 fatty acids, one can also obtain healthy fats from plant foods such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. The exclusion of seafood fits well with other motivations for avoiding overfishing, ocean environment devastation, and appreciation of sea creatures.
3. Lacto Products
Common lacto-products, such as milk, cheese, yogurt, butter, and cream, have to be substituted by a vegan diet. For instance, dairy is derived from animals. Again, dairy products are linked with various health problems, such as lactose intolerance, greater levels of cholesterol, and some cancers. Instead of dairy products, most vegans replace them with their plant-based equivalents, such as almond milk, soy yogurt, and vegan cheese, which are often supplemented with calcium and vitamin D, just like their regular dairy counterparts.
4. Eggs
There is an absolute prohibition of eggs, starting from chicken to duck and all sorts of poultry, in a fully vegan diet. Eggs are rich in cholesterol and animal proteins, and replacement options with plant-based proteins such as tofu, lentils, and chickpeas may very well be avoided. Ethical considerations apart, most eggs also come from factory farms; hence, it is fairly justified why eggs cannot be allowed in the lifestyle.
5. Honey
Honey is an animal byproduct of bees and is on the list of no-goes of a vegan diet. That honey is a natural sweetener is quite irrelevant here since bees are exploited in commercial production methods, so for ethical veganism, there cannot be an excuse for eating honey. In such a case, there are other agents of sweetness like maple syrup, agave nectar, or molasses.
Benefits of Following a Vegan Meal Plan
A vegan meal plan is a plant-based diet that never incorporates any form of animal products or by-products. Instead, it emphasizes nutrient-dense whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. This diet has vast health, environmental, and ethical benefits. So, let’s focus now on the really research-backed benefits:
1. Healthier Heart Condition
This is one of the greatest advantages of a vegan diet-it contributes to a good diet for a healthy heart. A vegan diet has no animal fats and cholesterol, which studies have proven often results in higher levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), known as the “bad” cholesterol. Due to saturated fats in meat and dairy that are generally avoided in the diet by a vegan, it might lead to lower cholesterol in the blood, facilitating a reduced risk of heart disease.
Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds are more plant-based food sources. These are all rich in antioxidants and fiber—both known to reduce blood pressure and enhance cardiac function. Compared with people who consume an omnivorous diet, vegans are at a 32% risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
2. Weight Loss and Management
Nothing is better than a vegan diet; it is a low-calorie diet but high in fiber, which is good for losing weight and preventing the same. Fruits, vegetables, and legumes are full of fibers, giving one a feeling of fullness while avoiding excessive consumption of processed foods and animal high-fat products.
Studies show that a vegan diet mostly goes hand-in-hand with low BMI values in people compared to others who are on diet schemes. The study further concluded that vegans are more likely to lose weight and also retain the weight off for an infinitely longer period when compared with non-vegans. Such a high fiber concentration in plant-based food helps one avoid over-eating, and high fiber content in their diet makes sound digestion inside their body.
3. Environmental Benefits
The third major benefit of a vegan diet plan is being environmentally friendly. Animal agriculture is linked to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water utilization. Plant-based food consumption may decrease people’s carbon footprint tremendously. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) indicates that livestock accounts for about 14.5 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions globally.
This means that the land and water required for land and water use are massively reduced in a vegan diet compared to animal and dairy production. Reducing demand for animal-based products contributes to biodiversity conservation and diminishes the pollution associated with factory farming.
4. Lower Disease of Chronic Conditions
Well-planned vegan diets minimize the risk of many chronic diseases. Indeed, a diet largely based on plant foods has been established as inversely associated with the development of type 2 diabetes, specific cancers, and hypertension. In vegan foods, phytonutrients, antioxidants, and fiber regulate blood sugar properly and assist the body in fighting oxidative stress, which leads to chronic diseases.
For instance, plant-based diets decrease the chance of getting colorectal cancer because they are fiber-rich; therefore, they help facilitate a healthy digestive process and bowel movements. In addition, other studies have established that being a vegan lowers the risk of developing one’s ability to create insulin resistance, which is one of the largest risks when it comes to the disease of type 2 diabetes.
Expert Review on Vegan Diet Plan
According to leading nutritionist Dr. Amit, note that there are some potential deficiencies concerning nutrient uptake, such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, which may be less readily available from plant sources. A well-placed vegan diet could provide all the necessary nutrients and many health benefits, such as reduced risks of chronic diseases and good weight control. Some no doubt obtain a nutritionally adequate diet through the means of fortified foods and diverse intakes of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. A visit to a healthcare provider could also garner specific advice in terms of the maintenance of health via veganism.
References
Hever, Julieanna. 2016. “Plant-Based Diets: A Physician’s Guide – PMC.” NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4991921/.
McManus, Katherine D., and Howard E. LeWine. 2024. “What is a plant-based diet and why should you try it?” Harvard Health. https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/what-is-a-plant-based-diet-and-why-should-you-try-it-2018092614760.
Meeks, Sade. 2021. “Vegan meal plan: Guide and meal suggestions.” MedicalNewsToday. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/vegan-meal-plan.
FAQs
1. What do I eat on a vegan diet?
On a vegan diet, you should eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, grains, and plant-based alternatives to dairy products. Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables daily, and choose whole grains when possible.
2. What is an example of a vegan diet?
A vegan diet includes plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Popular meals include quinoa salads, tofu stir-fry, and lentil soups.
3. Can vegans eat rice?
Yes, rice is a vegan-friendly food. It is commonly used in vegan dishes and pairs well with a variety of vegetables and legumes.
4. What is the Indian vegan diet?
An Indian vegan diet focuses on plant-based foods like grains, pulses, fruits, vegetables, and nuts while excluding all animal products.