Cauliflower is not only full of fiber but also very rich in vitamins C, K, and B6. Another thing it’s best known for is its potential as a low-calorie substitute for high-calorie foods like rice. This makes cauliflower great for weight loss. Cauliflower is ultimately a low-carb vegetable, making it keto-friendly. So for people following this diet, here are some nice cauliflower recipes to try.
Nutritional Value of Cauliflower
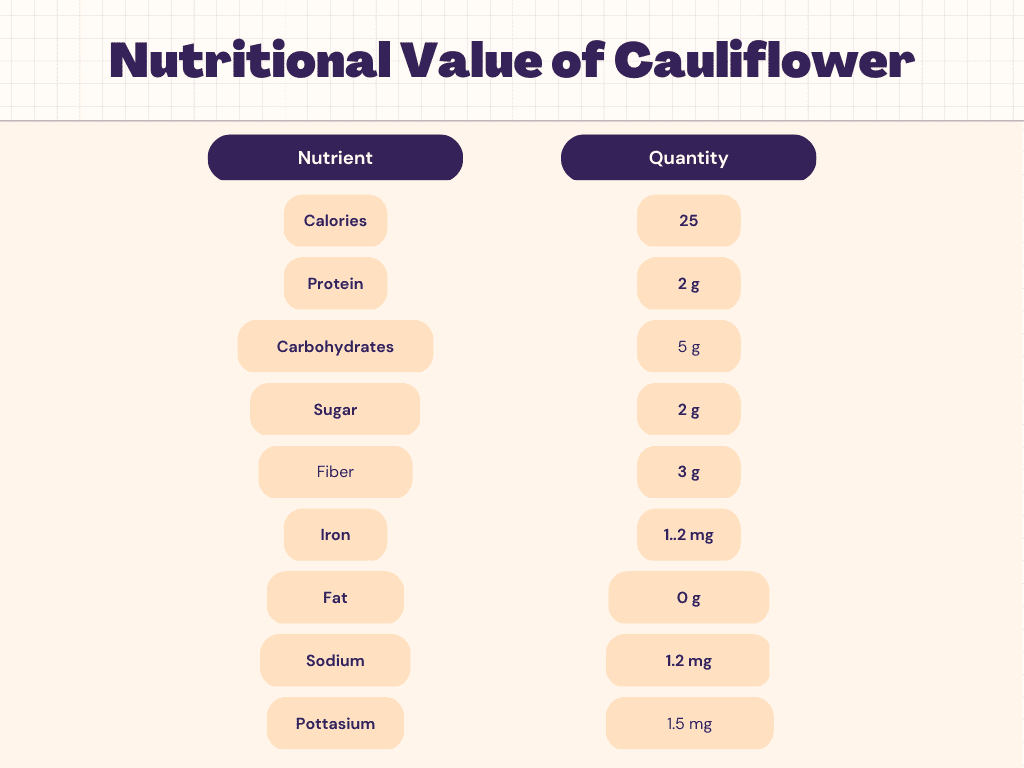
Nutritional Facts about Cauliflower
Carbs
Like all vegetables, cauliflower is a carbohydrate. But it’s a non-starch complex variety that’s high in fiber and low in natural sugar. It has a low glycemic index, somewhere between 15 and 30, which means it won’t cause a blood sugar spike.
Fats
Cauliflower is only slightly fat and cholesterol free. Therefore, it can easily be added to a low-fat diet or a cholesterol-lowering diet.
Protein
Cauliflower has minimal protein. To meet your daily protein needs, you need to include other healthy sources of protein in your diet.
Calories
At 27 calories per cup, you’d need to eat a lot of cauliflower before it significantly affects your total calorie intake. A total of 65% of cauliflower calories come from carbohydrates, 26% from protein, and 10% from protein.
Health Benefits of Cauliflower
- Promotes health and helps in the prevention of Chronic care diseases – Dietary fiber is very well-preserved in cauliflower. Cauliflower fiber is recognized to have various additional health advantages that help prevent chronic diseases. It is necessary for proper digestion, regulation of blood sugar, management of weight, protection against cancer, and other advantages.
- Reduces the risk of Heart Diseases – Heart disease is one of the health issues that fiber helps prevent. According to research released in 2017, the way that dietary fiber affects the gut flora may help to improve cardiovascular health, at least in part.
- Helps with fine Aging – Cauliflower contains glucosinolate glucoraphanin, which is a precursor to the phytochemical sulforaphane (SFN). Sulforaphane has the potential to be employed in anti-aging treatments and aids in preventing damage brought on by excessive exposure to UV light from the sun.
Vitamins & Minerals in Cauliflower
Cauliflower is an excellent source of vitamin C. One cup provides more than half of the daily value of 75 mg for adult women and 90 mg for adult men. It also provides a good dose of vitamin B6 and magnesium.
Nor are these the only nutrients in cauliflower. This vegetable contains calcium, iron, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, copper, manganese, fluorine, and a large number of B vitamins.
The Bottom Line
Cauliflower is a fiber-rich plant that is low in fat and calories. It is an excellent source of vitamin C while providing a good dose of vitamin B6 and magnesium, as well as many other micronutrients.
FAQs
How much Cauliflower consumption is needed?
Cauliflower, a generally healthy vegetable with vitamins C and K, low in calories and high in fiber, has hidden risks for some people. One cup of cauliflower a week offers health benefits without the risks.
Should I eat Cauliflower before or after exercise?
Your body needs fiber, but not before a workout. Vegetables such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, or cauliflower can be difficult to digest and can make exercise uncomfortable. Use simpler vegetables such as well-cooked asparagus or potatoes.
What are the benefits of Cauliflower?
- It is a Health-promoting factor
- Reduces the risk of heart diseases
- Helps in the prevention of stress and chronic diseases
- Helps in reducing the effects of aging
- Helps in the prevention of Cancer