The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland in the neck that plays a critical role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. When the thyroid gland is not functioning correctly, it can result in a range of symptoms of thyroid(signs of thyroid) and health problems, collectively known as thyroid(thyroid meaning) disorders. These disorders can arise due to various factors, including autoimmune diseases, iodine deficiency, genetic factors, and radiation exposure. This article will explore the meaning of the thyroid, its functions, symptoms associated with thyroid disorders, and the most common causes of these disorders(thyroid causes).
What is Thyroid?
Thyroid disease refers to a group of disorders that affect the function of the thyroid gland(thyroid meaning), a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and other vital functions. When the thyroid gland is not functioning correctly, it can cause a range of health problems and symptoms of thyroid.
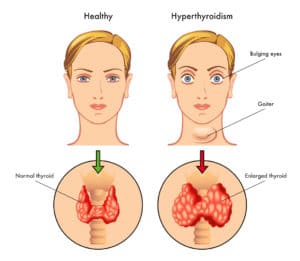
There are several types of thyroid disorders, including hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer. Hyperthyroidism(thyroid meaning) occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much hormone, while hypothyroidism occurs when the gland does not produce enough hormone. Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths that develop within the thyroid gland, and thyroid cancer is a relatively rare but potentially serious form of cancer that can develop in the thyroid gland.
Thyroid disorders(thyroid meaning) can affect individuals of any age or gender, but they are more common in women and tend to increase in frequency with age. These disorders can have a significant impact on a person’s overall health and quality of life, so it is essential to recognize the symptoms of thyroid and seek medical attention if they arise. Thyroid Treatment (thyroid meaning) varies depending on the specific disorder but may include medication, surgery, or radiation therapy.
What does Thyroid do?
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions by producing and secreting two hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are involved in controlling the body’s metabolism, which is the process by which the body converts food into energy.
When thyroid hormone levels are normal, they help regulate the body’s temperature, heart rate, and metabolism. They also aid in the growth and development of the body’s organs and tissues, including the brain and nervous system.
If the thyroid gland produces too much hormone (hyperthyroidism), it can lead to symptoms of thyroid such as weight loss, increased heart rate, anxiety, and tremors. On the other hand, if the gland produces too little hormone (hypothyroidism), it can lead to symptoms of thyroid(signs of thyroid) such as weight gain, fatigue, cold intolerance, and depression.
The thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain that produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH signals the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones, helping to maintain a balance of hormones in the body.
Overall, the thyroid gland plays a critical role in regulating many of the body’s functions and maintaining overall health. Any dysfunction of the thyroid gland can lead to a range of symptoms of thyroid(thyroid meaning) and health problems, which is why it is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a thyroid disorder.
How common is Thyroid Disease?
Thyroid disorders are becoming increasingly common in recent years. It is estimated that approximately 20 million Americans have some form of thyroid disease(thyroid meaning), and up to 60% of those affected are unaware of their condition.
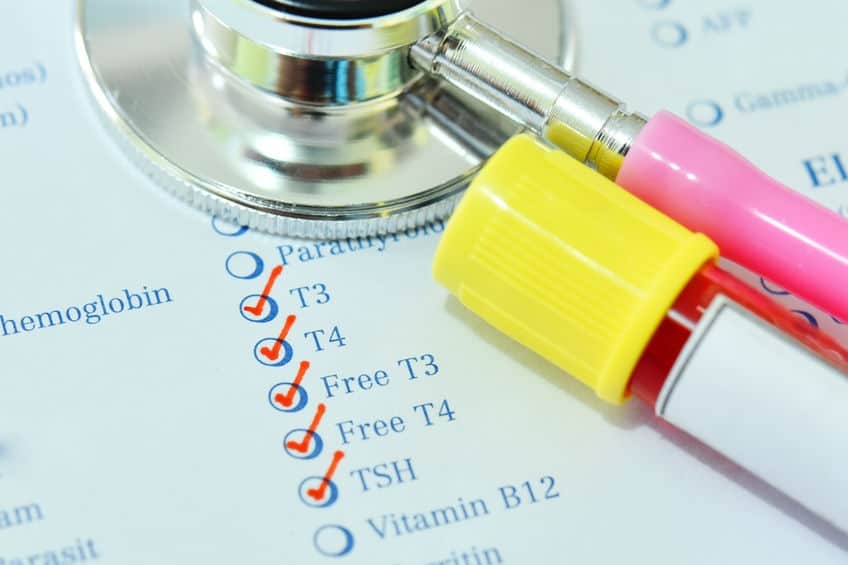
There are several reasons why thyroid disorders are becoming more prevalent. One factor is that diagnostic tools, such as thyroid test at home and imaging technologies, have become more sensitive and accurate in detecting thyroid problems(thyroid meaning). This has led to a higher rate of detection and diagnosis of thyroid disease.
Another contributing factor is that lifestyle changes and environmental factors can influence thyroid function. For example, exposure to radiation and certain chemicals, such as perchlorate and fluoride, can affect thyroid function. Additionally, iodine deficiency, which is becoming more common in many parts of the world, can impair thyroid function and lead to hypothyroidism.
Finally, genetics and family history can also play a role in the development of thyroid disease. Some types of thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, have a genetic component and tend to run in families.
Overall, while the exact causes of the increasing prevalence of thyroid disorders(thyroid causes) are complex and multifactorial, it is clear that thyroid disease is a significant public health issue that requires continued attention and research.
Who is affected by Thyroid disease?
Thyroid disorders can affect individuals of any age or gender, but some groups are at higher risk than others. Women are more likely than men to develop thyroid(thyroid meaning) disorders, with estimates suggesting that women are up to eight times more likely to be affected.
Thyroid disorders can also affect people of all ages, although some types of thyroid disorders are more common in specific age groups. For example, hyperthyroidism(thyroid meaning), which is characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, is more common in people under the age of 50, while hypothyroidism, which is characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, is more common in people over the age of 60.
People with a family history of thyroid disorders are also at increased risk of developing a thyroid problem themselves. Certain types of thyroid disorders, such as Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, have a genetic component and tend to run in families.
In addition, some lifestyle and environmental factors can increase the risk of developing a thyroid disorder. For example, exposure to radiation, certain chemicals, and iodine deficiency can all impair thyroid function and increase the risk of developing a thyroid disorder.
Overall, while thyroid disorders can affect anyone, some groups, including women, older adults, and those with a family history of thyroid disease, are at higher risk. It is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of thyroid disorders(signs of thyroid/thyroid causes) and to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have a thyroid problem.
How does Thyroid affect the body?
The thyroid gland produces hormones that play a critical role in regulating various bodily functions. When the thyroid gland is not functioning correctly, it can lead to a range of symptoms of thyroid(thyroid meaning) and health problems.
Thyroid disorders can affect different parts of the body in different ways. Some of the common ways that thyroid disorders can affect the body include:
- Metabolism: Thyroid hormones regulate the body’s metabolism, which is the process by which the body converts food into energy. When the thyroid gland produces too much hormone (hyperthyroidism), it can lead to an overactive metabolism and symptoms of thyroid(signs of thyroid) such as weight loss, sweating, and tremors. On the other hand, when the thyroid gland produces too little hormone (hypothyroidism), it can lead to an underactive metabolism and thyroid symptoms such as weight gain, fatigue, and feeling cold.
- Heart: Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating the heart’s function, including heart rate and rhythm. When the thyroid gland produces too much hormone (hyperthyroidism), it can lead to an increased heart rate, palpitations, and arrhythmias. Over time, this can lead to complications such as heart failure. On the other hand, when the thyroid gland produces too little hormone (hypothyroidism), it can lead to a slow heart rate and an increased risk of developing heart disease.
- Brain and Nervous System: Thyroid hormones are essential for the development and function of the brain and nervous system. When the thyroid gland produces too little hormone (hypothyroidism), it can lead to thyroid symptoms(signs of thyroid/thyroid causes) such as cognitive impairment, depression, and anxiety.
- Muscles and Joints: Thyroid hormones are also involved in the development and function of muscles and joints. When the thyroid gland produces too little hormone (hypothyroidism), it can lead to thyroid symptoms(thyroid meaning) such as muscle weakness, stiffness, and joint pain.
- Skin and Hair: Thyroid hormones also play a role in maintaining healthy skin and hair. When the thyroid gland produces too little hormone (hypothyroidism), it can lead to dry skin, brittle nails, and hair loss.
Overall, the thyroid gland and its hormones play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. When the thyroid gland is not functioning correctly, it can lead to a range of thyroid symptoms(signs of thyroid) and health problems, highlighting the importance of early detection and treatment of thyroid disorders.
What are the major Symptoms of Thyroid?
Here are some of the major symptoms of thyroid disorders:
- Weight changes: Unexplained weight loss or gain, despite no changes in diet or activity level, can be a symptom of a thyroid problem.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or exhausted, even after getting enough sleep, can be a sign of a thyroid disorder.
- Mood changes: Thyroid disorders can cause mood swings, anxiety, irritability, and depression.
- Changes in heart rate: Thyroid disorders can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Changes in body temperature: Hypothyroidism can cause feeling cold, while hyperthyroidism can cause feeling hot and excessive sweating.
- Changes in bowel movements: Thyroid disorders can cause constipation or diarrhea.
- Muscle weakness: Thyroid disorders can cause muscle weakness, especially in the arms and legs.
- Changes in the menstrual cycle: Women with thyroid disorders may experience irregular periods or heavy bleeding.
- Changes in skin and hair: Thyroid disorders can cause dry skin, hair loss, and brittle nails.
- Swelling in the neck: Enlargement of the thyroid gland can cause a visible lump or swelling in the neck area.
If you experience any of these thyroid symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation. These symptoms may indicate a thyroid disorder or another underlying medical condition that requires treatment.
Thyroid Symptoms in Female
Thyroid disorders(thyroid symptoms in women/thyroid symptoms in female) are more common in women than in men and can affect females of any age. Some of the common symptoms of thyroid disorders in females include:
- Changes in the menstrual cycle: Thyroid disorders can affect the menstrual cycle, causing irregular periods, heavy bleeding, or even the absence of periods.
- Changes in weight: Thyroid disorders can cause unexplained weight gain or weight loss, despite no changes in diet or physical activity.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or exhausted, even after getting enough sleep, is a common symptom of thyroid disorders.
- Mood changes: Thyroid disorders can cause mood swings, anxiety, irritability, and depression.
- Changes in body temperature: Hypothyroidism can cause feeling cold, while hyperthyroidism can cause feeling hot and excessive sweating.
- Changes in skin and hair: Thyroid disorders can cause dry skin, hair loss, and brittle nails.
- Swelling in the neck: Enlargement of the thyroid gland can cause a visible lump or swelling in the neck area.
- Muscle weakness: Thyroid disorders can cause muscle weakness, especially in the arms and legs.
- Changes in heart rate: Thyroid disorders can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you experience any of these thyroid symptoms((thyroid symptoms in women/thyroid symptoms in female), it is important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation. These thyroid symptoms((thyroid symptoms in women/thyroid symptoms in female)) may indicate a thyroid disorder or another underlying medical condition that requires treatment.
Thyroid Symptoms in Male
Thyroid disorders can affect males as well as females, although they are more common in women. Some of the common symptoms of thyroid disorders in males include:
- Changes in weight: Thyroid disorders can cause unexplained weight gain or weight loss, despite no changes in diet or physical activity.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or exhausted, even after getting enough sleep, is a common symptom of thyroid disorders.
- Mood changes: Thyroid disorders can cause mood swings, anxiety, irritability, and depression.
- Changes in body temperature: Hypothyroidism can cause feeling cold, while hyperthyroidism can cause feeling hot and excessive sweating.
- Changes in skin and hair: Thyroid disorders can cause dry skin, hair loss, and brittle nails.
- Swelling in the neck: Enlargement of the thyroid gland can cause a visible lump or swelling in the neck area.
- Muscle weakness: Thyroid disorders can cause muscle weakness, especially in the arms and legs.
- Changes in heart rate: Thyroid disorders can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you experience any of these thyroid symptoms(thyroid symptoms in men/thyroid symptoms in male), it is important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation. These thyroid symptoms(thyroid symptoms in men/thyroid symptoms in male) may indicate a thyroid disorder or another underlying medical condition that requires treatment.
Thyroid Symptoms in Teens & Children
Thyroid problems can occur in teenagers and children and can have a significant impact on their growth and development. Some of the symptoms of thyroid problems in teens and children may include:
- Delayed growth and development: Thyroid problems can affect a child’s growth and development, leading to delays in height and weight.
- Delayed puberty: Thyroid problems can also delay the onset of puberty in both boys and girls.
- Fatigue: Children and teens with thyroid problems may feel tired or sluggish, even after getting enough sleep.
- Weight gain: Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight can be a symptom of thyroid problems in children and teens.
- Hair loss: Thinning hair or hair loss, particularly from the scalp, eyebrows, and other areas of the body.
- Constipation: Constipation or difficulty passing stools can be a symptom of thyroid problems in children and teens.
- Mood changes: Changes in mood, including irritability, anxiety, and depression.
- Learning and memory problems: Thyroid problems can affect a child’s ability to learn and remember things.
- Swelling of the thyroid gland: A swollen thyroid gland (goiter) can be a sign of thyroid problems in children and teens.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by other medical conditions as well, so it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. If you suspect that your child or teen may have a thyroid problem, it’s important to schedule an appointment with their healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Thyroid Symptoms in Infants
Thyroid problems can also occur in infants, and can have a significant impact on their growth and development. The most common thyroid problem in infants is congenital hypothyroidism, which is a condition where the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormone from birth. Some of the symptoms of congenital hypothyroidism in infants may include:
- Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Poor feeding: Infants with congenital hypothyroidism may have difficulty feeding or may not want to eat at all.
- Swollen tongue: The tongue may appear larger than normal.
- Puffy face: The face may appear swollen or puffy.
- Constipation: Constipation or difficulty passing stools.
- Delayed growth and development: Infants with congenital hypothyroidism may have delays in growth and development.
- Hoarse cry: The cry may sound hoarse or weak.
- Cold intolerance: Infants with congenital hypothyroidism may have a lower tolerance for cold temperatures than normal.
- Low muscle tone: The muscles may feel soft or floppy.
- Breathing problems: Infants with congenital hypothyroidism may have difficulty breathing or may breathe rapidly.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by other medical conditions as well, so it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. If you suspect that your infant may have a thyroid problem, it’s important to schedule an appointment with their healthcare provider as soon as possible.
What causes Thyroid?
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of thyroid disorders, including:
- Autoimmune disorders: Autoimmune disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease are the most common causes of thyroid disorders(thyroid causes). In these disorders, the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage to the gland.
- Iodine deficiency: Iodine is a crucial nutrient required for the production of thyroid hormones. If the body does not get enough iodine, the thyroid gland may not be able to produce enough hormones, leading to hypothyroidism.
- Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, whether from medical treatments or environmental sources, can damage the thyroid gland and lead to thyroid disorders.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can interfere with thyroid function and lead to thyroid disorders.
- Genetics: Thyroid disorders can run in families, and some people may be more genetically susceptible to developing thyroid disorders.
- Age and gender: Thyroid disorders are more common in women than in men, and the risk of developing a thyroid disorder increases with age.
It is important to note that in many cases, the exact cause of thyroid disorders is not known. If you have a family history of thyroid disorders or are experiencing symptoms of a thyroid disorder, it is important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation and diagnosis.
Tips for a healthy Thyroid
Here are some tips for maintaining a healthy thyroid:
- Eat a balanced diet: Consuming a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients such as iodine, selenium, and zinc can help support thyroid function. Foods like seafood, dairy, eggs, nuts, and whole grains are good sources of these nutrients.
- Avoid excessive intake of goitrogens: Goitrogens are compounds found in certain foods, such as cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale, that can interfere with thyroid function when consumed in excess. While it’s generally safe to eat these foods in moderation, excessive intake may be problematic for some people with thyroid disorders.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can interfere with thyroid function and exacerbate symptoms of thyroid disorders. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help support thyroid health.
- Get enough sleep: Sleep is essential for overall health, and studies have shown that insufficient sleep can negatively impact thyroid function. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support thyroid health.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise has been shown to support thyroid function and can help reduce the risk of developing thyroid disorders. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Check your iodine levels: Iodine is a crucial nutrient for thyroid function, and iodine deficiency is a common cause of thyroid disorders. If you’re concerned about your iodine levels, speak with your healthcare provider about getting tested.
- Take medications as prescribed: If you have been diagnosed with a thyroid disorder and are taking medication to manage your thyroid symptoms(thyroid symptoms in men/thyroid symptoms in male), be sure to take your medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Skipping doses or altering your dosage without medical guidance can be harmful to your thyroid health.
Try To Limit “Ultra-Processed” Foods
Ultra-processed foods are foods that contain high amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives, and are typically low in essential nutrients. These foods can contribute to inflammation in the body, which can interfere with thyroid function and exacerbate symptoms of thyroid disorders.
Instead, focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats can help support thyroid health. These foods contain important nutrients like iodine, selenium, and zinc that are essential for thyroid function, as well as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that can help reduce inflammation in the body.
In addition, limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking can also be beneficial for thyroid health, as these behaviors can interfere with thyroid function and contribute to inflammation in the body. Regularly monitoring your thyroid function with blood tests and speaking with your healthcare provider about any concerns or thyroid symptoms(thyroid symptoms in men/thyroid symptoms in male) you may be experiencing can also help ensure optimal thyroid health.
Get Enough Iron In Your Diet
Yes, getting enough iron in your diet is important for thyroid health. Iron is an essential nutrient that is required for the production of thyroid hormones. If the body does not get enough iron, it may not be able to produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to hypothyroidism.
Good sources of iron include lean meats, poultry, fish, legumes, nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables. It is important to pair these foods with vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits or bell peppers, as vitamin C can enhance iron absorption in the body.
It is also important to note that excessive iron intake can be harmful to thyroid health, so it is important to consume iron in moderation and speak with your healthcare provider if you have concerns about your iron levels.
In addition to iron, other nutrients like selenium, zinc, and copper are also important for thyroid function. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods can help ensure that you are getting all of the essential nutrients you need to support optimal thyroid health.
Consider a Selenium Supplement
Selenium is an important mineral that is required for thyroid hormone production and metabolism. Studies have shown that selenium supplementation can help improve thyroid function and may be beneficial for individuals with thyroid disorders, particularly those with autoimmune thyroiditis.
However, it is important to note that excessive selenium intake can also be harmful, so it is important to speak with your healthcare provider before starting a selenium supplement. They can help determine whether a selenium supplement is necessary and what dosage would be appropriate for you.
In addition, it is always best to obtain nutrients from whole foods whenever possible. Good dietary sources of selenium include Brazil nuts, seafood, poultry, and whole grains.
It is also important to note that while selenium may be beneficial for some individuals with thyroid disorders, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. If you have a thyroid disorder, it is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
What are the risk factors associated with Thyroid?
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing thyroid disorders(thyroid symptoms in female):
- Gender: Women are much more likely than men to develop thyroid disorders, particularly autoimmune thyroiditis, and hypothyroidism.
- Age: Thyroid disorders can occur at any age, but the risk increases with age, particularly for hypothyroidism.
- Family history: If a close family member, such as a parent or sibling, has a thyroid disorder, there is an increased risk of developing one as well.
- Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, particularly during childhood or adolescence, can increase the risk of developing thyroid cancer or other thyroid disorders.
- Iodine intake: Iodine is an essential nutrient that is required for thyroid hormone production. Both insufficient and excessive iodine intake can increase the risk of thyroid disorders.
- Autoimmune diseases: Having an autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of developing autoimmune thyroiditis.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can interfere with thyroid function and increase the risk of thyroid disorders.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy can affect thyroid function, and women who have had thyroid problems in the past or have a family history of thyroid disorders may be at increased risk during pregnancy.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that an individual will develop a thyroid disorder. However, individuals who have these risk factors may benefit from regular thyroid function testing and close monitoring of their thyroid health.
Who gets Thyroid Disease?
Thyroid disorders can occur in anyone, regardless of age, gender, or race. However, there are certain populations that are more prone to thyroid disorders than others.
Women are much more likely than men to develop thyroid disorders, particularly autoimmune thyroiditis and hypothyroidism. Additionally, the risk of developing thyroid disorders increases with age, particularly for hypothyroidism.
Individuals with a family history of thyroid disorders are also more prone to developing thyroid problems themselves. Exposure to radiation, particularly during childhood or adolescence, can increase the risk of developing thyroid cancer or other thyroid disorders.
Iodine intake is also an important factor in thyroid health, and both insufficient and excessive iodine intake can increase the risk of thyroid disorders.
Furthermore, individuals with autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, are more prone to developing autoimmune thyroiditis. Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can also interfere with thyroid function and increase the risk of thyroid disorders.
Pregnancy can also affect thyroid function, and women who have had thyroid problems in the past or have a family history of thyroid disorders may be more prone to thyroid problems during pregnancy.
It is important to note that while certain populations may be more prone to developing thyroid disorders, anyone can develop a thyroid disorder. If you are experiencing symptoms of thyroid dysfunction or have concerns about your thyroid health, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider.
FAQs
Can Thyroid symptoms appear suddenly?
In some cases, thyroid symptoms(thyroid symptoms in male/thyroid symptoms in women/thyroid symptoms in female) can appear suddenly. This is particularly true for hyperthyroidism, which is an overactive thyroid gland. Some individuals with hyperthyroidism may experience a sudden onset of thyroid symptoms(thyroid symptoms in male/(thyroid symptoms in women/thyroid symptoms in female), such as rapid heart rate, anxiety, tremors, and weight loss. In rare cases, individuals may experience a sudden and life-threatening complication of hyperthyroidism known as thyroid storm, which can cause fever, confusion, rapid heart rate, and other serious symptoms.
In contrast, hypothyroidism, which is an underactive thyroid gland, typically develops slowly over time and may not cause noticeable symptoms for many years. However, in some cases, individuals with hypothyroidism may experience a sudden worsening of symptoms, such as extreme fatigue, depression, and weight gain.
It is important to note that the sudden onset of symptoms can also be a sign of other medical conditions, so it is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you experience any sudden changes in your health. If you are experiencing symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, your healthcare provider can perform thyroid function tests to determine if thyroid dysfunction is the underlying cause. Read about science of thyroid.
What are the Early Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid?
The signs and symptoms of thyroid dysfunction can vary depending on whether the thyroid gland is overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism). Here are some of the early signs and symptoms of thyroid dysfunction:
Early Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Increased sweating
- Trembling or shaking
- Anxiety or nervousness
- Difficulty sleeping or insomnia
- Unexplained weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea
- Lighter or absent menstrual periods in women
- Muscle weakness or fatigue
- Sensitivity to heat
- Eye problems, such as bulging or dryness
Early Signs and Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Dry skin or hair
- Hair loss
- Muscle aches or stiffness
- Depression or irritability
- Memory problems or difficulty concentrating
- Irregular or heavy menstrual periods in women
- Slowed heart rate
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other medical conditions, so it is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you are experiencing any of these thyroid symptoms in female. Your healthcare provider can perform thyroid function tests to determine if thyroid dysfunction is the underlying cause.
What are the common symptoms of Thyroid?
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Dry skin or hair
- Hair loss
- Muscle aches or stiffness
- Depression or irritability
- Memory problems or difficulty concentrating
- Irregular or heavy menstrual periods in women
- Slowed heart rate
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other medical conditions, so it is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. Your healthcare provider can perform thyroid function tests to determine if thyroid dysfunction is the underlying cause.
What else can cause Thyroid?
There are various factors that can cause thyroid dysfunction, including:
- Autoimmune diseases: The most common cause of thyroid disorders is autoimmune diseases, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, which occur when the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
- Genetics: Thyroid disorders can run in families, and certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing thyroid dysfunction.
- Radiation therapy: Exposure to high levels of radiation, such as radiation therapy for cancer treatment or exposure to radiation from nuclear accidents, can damage the thyroid gland and lead to thyroid dysfunction.
- Medications: Some medications, such as amiodarone, lithium, and interferon-alpha, can affect the function of the thyroid gland and lead to thyroid dysfunction.
- Iodine deficiency or excess: The thyroid gland requires iodine to produce thyroid hormones, and an inadequate or excessive intake of iodine can lead to thyroid dysfunction.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy can cause changes in thyroid hormone levels, and some women may develop thyroid dysfunction during or after pregnancy.
- Aging: As people age, the risk of developing thyroid dysfunction increases.
It is important to note that the exact cause of thyroid dysfunction can be complex and may involve multiple factors. If you are experiencing symptoms of thyroid dysfunction, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. Become our new Thyroid Success Story!
What are some complications of Thyroid?
Untreated or poorly managed thyroid dysfunction can lead to several complications. The complications can vary depending on whether the thyroid gland is overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism). Here are some of the common complications associated with thyroid dysfunction:
Complications of Hyperthyroidism:
- Irregular heartbeat or heart failure
- Osteoporosis
- Thyroid storm (a rare but life-threatening condition characterized by high fever, rapid heartbeat, and altered mental status)
- Eye problems, such as bulging or double vision
Complications of Hypothyroidism:
- High cholesterol levels and increased risk of heart disease
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Myxedema coma (a rare but life-threatening condition characterized by low body temperature, slowed breathing, and altered mental status)
- Mental health problems, such as depression or dementia
- Birth defects in infants born to women with untreated hypothyroidism during pregnancy
It is important to note that with proper management and treatment, many of these complications can be prevented or minimized. If you are experiencing symptoms of thyroid dysfunction or have been diagnosed with a thyroid disorder, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan and monitor your condition to prevent complications.
How to control Thyroid in Males?
The treatment for thyroid dysfunction in males is generally the same as for females and depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Here are some ways to help control thyroid dysfunction in males:
- Medications: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed for hypothyroidism to replace the missing thyroid hormones. For hyperthyroidism, medications that suppress the production of thyroid hormones may be prescribed.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: This treatment involves taking radioactive iodine orally, which is absorbed by the thyroid gland and destroys the thyroid cells that produce hormones to reduce thyroid causes.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland(what is thyroid) may be necessary.
- Lifestyle changes: Eating a healthy diet, Thyroid Recipes, getting regular exercise, and managing stress can help support overall health and may help manage thyroid(what is thyroid) dysfunction.
- Regular monitoring: Regular blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels(what is thyroid) are important to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust medication dosages as needed.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan for thyroid dysfunction(what is thyroid) based on individual needs and underlying thyroid causes. Read more about this in our Thyroid Blogs.
How to control Thyroid in Females?
The treatment for thyroid dysfunction in females depends on the underlying cause of the condition, but there are several ways to help manage thyroid dysfunction:
- Medications: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed for hypothyroidism(what is thyroid) to replace the missing thyroid hormones. For hyperthyroidism, medications that suppress the production of thyroid hormones may be prescribed.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: This treatment involves taking radioactive iodine orally, which is absorbed by the thyroid gland(what is thyroid) and destroys the thyroid cells that produce hormones.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid(what is thyroid) gland may be necessary.
- Lifestyle changes: Eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress can help support overall health and may help manage thyroid dysfunction.
- Regular monitoring: Regular blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels(what is thyroid) are important to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust medication dosages as needed.
It is also important for females to manage other health conditions that may contribute to thyroid dysfunction(what is thyroid), such as autoimmune disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and pregnancy-related what is thyroid disorders. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan for thyroid dysfunction based on individual needs and underlying thyroid causes(what is thyroid).